Publications
- J. P. Chinta, B. Ramanujam and C. P. Rao,"Structural aspects of the metal ion complexes of the conjugates of calix[4]arene: Crystal structures and computational models",
Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 256(2012), 2762-2794.
- A. Acharya, K. Samanta and C. P. Rao,
"Conjugates of Calixarenes Emerging as Molecular Entities of Nanoscience",
Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 256(2012) 2096-2125. DOI:10.1016/j.ccr.2012.05.018
- R. Joseph and C. P. Rao, "Ion and Molecular Recognition by Lower Rim 1,3-Di-conjugates of Calix[4]arene as Receptors", Chem. Rev., 111(2011) 4658-4702, DOI:10.1021/cr1004524
Publications
Click on the title to view the abstracts; click again to hide it.
Show or hide all abstracts
-
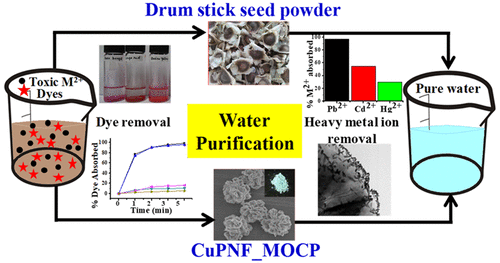 |
Seed powder of vegetable drum stick (Moringa oleifera) is a household known material for the coagulation of impurities from water. We find from our lab experiments that this material indeed removes toxic inorganic heavy metal ions and organic dyes; however, the latter can be degraded in the presence of H2O2 under Cu2+ as catalyst. To understand the details of the treatment of water that is taking place by this seed powder, a simple inorganic–protein nanoflower system was developed using copper phosphate (CuP), and a low molecular weight, cationic, and coagulant protein of Moringa oleifera (MOCP), to result in the nanoflowers (NFs), CuPNF_MOCP. The CuPNF_MOCPs were synthesized at different ratios of inorganic versus protein components and characterized by spectroscopy and microscopy techniques. Both the time- and the protein concentration-dependent flower growth showed complete flower morphology within 24 h with tightly packed petals having smooth surface upon increasing the protein concentration as noticed from SEM. The anionic dyes were adsorbed more preferentially over the cationic ones by these NFs, due to the cationic charge present on MOCP, as understood by studying six different dyes of which three are anionic and three are cationic in nature. The dyes are oxidatively degraded by a Fenton-type mechanism that takes place between Cu2+ present in the NFs and added H2O2 with the generation of •OH radicals. These NFs also adsorb heavy metal ions, such as Pb2+, Cd2+, and Hg2+, with high selectivity of >99% for Pb2+. Upon adsorption of Pb2+, the surface of the NFs revealed needle-shaped structures at petal edges in their micrographs, where the needles were confirmed by elemental mapping, powder XRD, and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Thus, the water purification routinely carried out by the households using the drum stick seed powder is essentially due to the coagulant protein present in it. This has been demonstrated in the form of CuPNF_MOCP for scavenging toxic heavy metal ions and organic dyes from water sources. Hence, this study provides a lead for the purification of water in a sustainable manner.
Go to article |
-
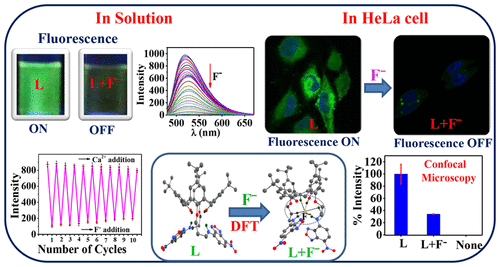 |
p-tert-Butyl-calix[4]arene was derivatized by integrating a benzooxadiazole fluorescent tag into its 1,3-arms at the lower rim to result in L and was characterized. L was titrated with 17 anions in THF and found selective for F– ions with lowest detection limit of 109 ppb. L and F– form a 1:1 complex. L self-assembles in THF to result in sheet like structures which converts into smaller spherical particles upon addition of F–. The site of interaction of F– was deduced based on 1H NMR spectroscopy and the coordination features by density functional theory (DFT) computations wherein six noncovalent interactions of the type X–H···F (where X = O, N, or C) were noticed. The sensing of F– is reversible when titrated with Ca2+, and the reversibility was demonstrated for 10 cycles without losing sensitivity. The study has been extended to the biological cells using fluorescence and confocal microscopy. While L shows strong fluorescence in HeLa cells, increasing concentrations of F– exhibited greater fluorescence quenching. Thus, L acts as a good sensor for F– in solution as well as in biological cells, a rare and unique combination for a calixarene conjugate to exhibit such sensing behavior in dual media.
Go to article |
-
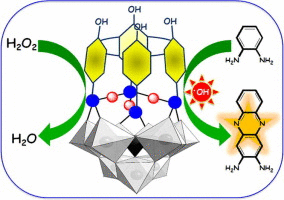 |
The inorganic-organic hybrid based on covalently attached trilacunary phosphotungstate and calixarene conjugate (POM-Calix hybrid) has been synthesized via facile click chemistry approach. The characterization studies showed that both the moieties are present together in the hybrid upon covalent modification. The morphology of the hybrid was studied by SEM, TEM and AFM analyses suggesting spherical shaped nanoparticles of 40–60 nm size for the hybrid. The POM-Calix hybrid was successfully employed to demonstrate peroxidase-like activity for the oxidation of the model substrate, viz., o-phenylenediamine (OPD), for the enzyme. The activity of the POM-Calix hybrid was ∼170% greater than that exhibited by simple POM and this is mainly attributed to the introduction of hydrophobic character by the covalently attached calixarene conjugate and the hydrophobicity is supported by the contact angle measurement. From the kinetic studies, the Michaelis constants, Km and Vmax were estimated to be 2.55 mM and 0.756 × 10−8 M s−1, respectively. It was observed that, the POM-Calix hybrid facilitates the formation of OH radicals when treated with H2O2 which eventually results in the oxidation of the substrate. The POM-Calix hybrid exhibits excellent enzyme-like activity over a wide pH range, which would enable its bio-applications at physiological conditions.
Go to article |
-
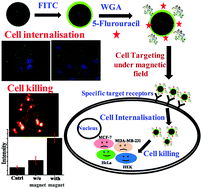 |
Lectins are known for their specificity for carbohydrate binding. However, a few specific carbohydrate residues are over expressed in cancer cells, which may be an advantage for using a lectin that is specific to such residues. Herein, we report the strategic design of wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) and a fluorescent torch, FITC immobilized on Fe3O4 NPs as a cell membrane specific receptor target for breast cancer cells, viz., MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. The resultant nanocomplexes were well characterized by using microscopy and spectroscopy. The WGA tagged nanocomplex was further loaded with the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) to selectively kill the cancer cells. The loading efficiency of 5-FU is ∼356 μg mg−1. The nanocomplex itself shows ∼90% cell viability for all the four cell lines (HEK, HeLa, MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) studied and is therefore a suitable targeting drug delivery vehicle. However, the nanocomplex loaded with {WGA + 5-FU} shows a ∼1.5-fold decrease in cell viability in the case of specific cells (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) when compared to non-specific cells (HeLa and HEK). The internalization of the nanocomplex is supported by fluorescence microscopy and confocal laser scanning microscopy techniques by tracking with the fluorescent torch, FITC. The nanocomplex can be internalized ∼2 times more in the specific cells as compared to the non-specific cells. It is observed that the internalization is ∼2 fold increased when the MDA-MB-231 cells are exposed to a magnetic field for 24 h as compared to in the absence of a magnetic field. Live–dead cell assay of the 5-FU loaded nanocomplex was done by propidium iodide (PI) staining. There is an increase in the cell death by ∼2.5 fold when the cells are under a magnetic field as measured from the PI uptake. Such strategic designing of the nanocomplex can lead to the development of a better method to selectively target and kill the cancer cells by acting as a carrier to deliver a suitable drug, as a result of which the medical field can benefit.
Go to article |
-
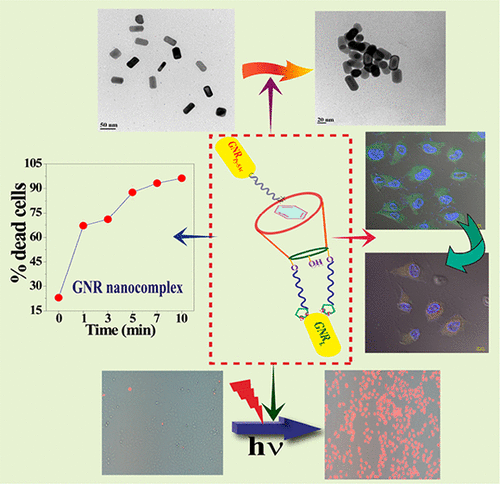 |
A new 1,3-lower rim-lipoic acid appended calix[4]arene (L) has been synthesized and characterized by different spectral techniques. Lipoic acid functionality helps L to anchor onto a noble metal surface, and in the present case these are the gold nanorods (GNRs). As the conjugate of calix[4]arene acts as a host due to the presence of its arene cavity, pyridinium containing guests have been explored to study their complexation, since the pyridinium containing molecules will accumulate in mitochondria in cells. The host–guest complexation has been explored in solution by 1H NMR, ESI-MS, UV–vis, and fluorescence spectral titration studies. The loading of host and the guest onto the GNR surface has been analyzed by spectroscopy and microscopy and found that their combination results in nanocomplexation. The presence of pyridinium functionality on the guest leads to targeted delivery to mitochondria of GNR nanocomposites as shown by confocal laser scanning microscopy imaging. The nanocomplex has been studied for cancer cell imaging and laser-induced cell killing with the help of plasmonic gold nanorods. When excited at the longitudinal SPR band of GNRs using laser (λ = 633 nm), cancer cell killing was observed due to laser-induced cell death. The flow cytometry studies supported ∼97% killing when the GNR-nanocomplex administered HeLa cells were irradiated under laser light for 10 min, which is a ∼4 fold increase in their cell as compared to the study carried out in the absence of laser light irradiation, and this has been partly attributed to the greater internalization of these into cells.
Go to article |
-
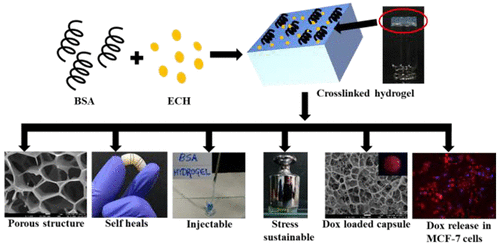 |
Hydrogels have been used in the literature in tissue engineering, in drug delivery, and as enzyme biomimics. Herein, we report the synthesis of a functional biomaterial using BSA as scaffold and epichlorohydrin as cross-linker. The hydrogels reported in this paper were shown to exhibit tunable pore size as a function of BSA concentration by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and, therefore, are well suited to encapsulate drug molecules for delivery applications. These are injectable, shear thinning, self-healing, and has the ability to withstand a physical weight of ∼300 times of its own. In trypsin medium, the gel is degraded by 50% in 36 h supporting that these are biodegradable. The loading of Dox by the gel was confirmed by the emission of red fluorescence and also by filling the pores by fibrillar structures as demonstrated by SEM. The controlled release of Dox occurs over 5 days to an extent of 37 ± 2%, 26 ± 0.5%, and 21 ± 1.5% in PBS at pH 5.5, 6.8, and 7.4 respectively. Since these hydrogels are made of BSA as matrix, their biocompatibility was proven by MCF-7, HeLa, and MDA-MB-231 cells wherein 95 ± 5% of cells are viable when treated with unloaded hydrogel. However, the Dox loaded hydrogel results in 70–80% of killing in the case of all three cancer cells. Fluorescence microscopy and FACS studies support controlled and time dependent release of Dox in MCF-7 cells for 24 h where the drug goes into cytoplasm initially and then into nucleus. The cell cycle analysis carried out using MCF-7 cells clearly showed that the cell death is due to apoptosis, and this is by arresting the G2/M phase as a function of time. All of the data supports the utility of the synthesized BSA hydrogel as a biomaterial that will find application in controlled drug delivery.
Go to article |
-
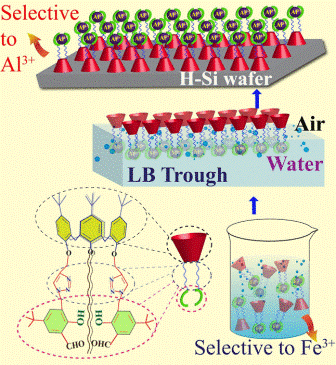 |
A triazole appended benzaldehydic lower rim derivative of calix[4]arene (L) has been synthesized and was thoroughly characterized. In CH3CN solution, the L showed greater sensitivity for Fe3+ by a 5‐fold increase in the absorbance and 37% quenching in the fluorescence intensity, by forming a 1:1 complex. The Fe3+ induces aggregation in L as studied by microscopy. The Langmuir film formed at the air‐water interface was characterized by pressure‐area isotherm and Brewster angle micrographs, both in the presence and absence of metal ions. The Langmuir films of pure L, {L+Al3+} and {L+Zn2+} were transferred onto H‐terminated Si‐wafer and characterized using Atomic Force Microscopy, contact angle, Grazing Incidence Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrscopy and X‐ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. The study resulted selective binding of Al3+ to the Langmuir film of L among the nine metal ions studied. Thus, the calix[4]arene‐conjugate L is sensitive and selective to Fe3+ in acetonitrile solution whereas to Al3+ in Langmuir film and hence acts as an ion switch depending upon the physical state of L.
Go to article |
-
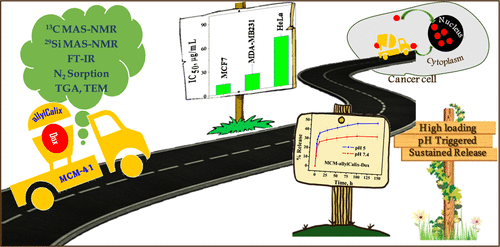 |
An inorganic–organic hybrid material, MCM-allylCalix, was synthesized by covalent modification of an MCM-41 surface with a tetra-allyl calixarene conjugate. The synthesized hybrid was characterized by 13C and 29Si MAS–NMR, Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses. The application of this MCM-allylCalix hybrid has been demonstrated for loading and in vitro release of doxorubicin (Dox) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) buffer as well as in the cancer cells, viz., MCF7, HeLa, and MDA-MB231. The Dox-loaded hybrid, MCM-allylCalix-Dox, was characterized by TEM, FT-IR, TGA, N2 sorption, diffuse refectance spectroscopy–UV, and fluorescence microscopy to confirm the presence of the drug. The release study of the drug from MCM-allylCalix-Dox was carried out in PBS buffer at pH 5 and 7.4. The results showed ∼140% increase in the release of Dox at pH 5 compared to that at pH 7.4 in 144 h, suggesting a pH-triggered release of the drug. MCM-allylCalix-Dox releases a greater amount of Dox compared to that released from unmodified MCM-Dox. Cytotoxicity studies suggested that MCM-allylCalix-Dox exhibits anticancer activity that is dependent on the nature of the cell. The Dox-loaded hybrid shows more cytotoxicity for MCF7 compared to that for the HeLa and MDA-MB231 cells. This was further supported by ∼120% more internalization of Dox into MCF7 cells compared to that in the other two cell lines. Both fluorescence microscopy and fluorescence-activated cell sorting studies suggested concentration-dependent internalization of Dox into the MCF7 and HeLa cells. The results suggested that the inorganic–organic hybrid can be useful in sustained drug delivery into cancer cells.
Go to article |
-
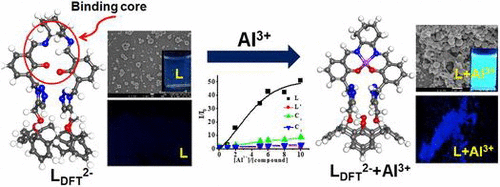 |
A cyclohexane-trans-1,2-diimine capped conjugate of 1,3-calix[4]arene (L) has been synthesized and characterized using different analytical and spectral techniques. L has been shown to be sensitive toward Al3+ by exhibiting ~45-fold enhancement in its emission intensity at 445 nm upon complexation. All the other 15 metal ions showed almost no or minimal change in the fluorescence intensity of the L supporting that none of those 15 ions is sensed by L. The complexation between L and Al3+ has been further confirmed by absorption spectroscopy, isothermal titration calorimetry and ESI MS. The isotopic peak pattern of the ESI MS peak clearly confirmed the presence of aluminum in the 1:1 complex formed. The need for the flexible cap moiety for bringing selectivity to Al3+ was proven by comparing the titration studies with the corresponding control molecules. The sensing of Al3+ by L in the solid powder was demonstrated by fluorescence microscopy. The supramolecular behavior of L changes from simple spherical type morphology in L to an aggregated micro pots and fibers upon Al3+ binding. The DFT computational study yielded a distorted tetrahedral complex of the dianionic receptor resulting in AlN2O2 core.
.
Go to article |
-
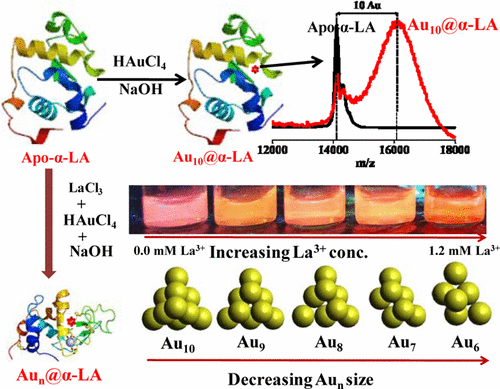 |
In this paper, we report the studies relevant to controlling the size of protein-protected gold nanoclusters (AuNCs). In order to demonstrate this, we have chosen bovine apo α-Lactalbumin (apo-α-LA), which has a specific binding site for Ca2+, and La3+ occupies this position when apo-α-LA is treated with lanthanum trichloride. When the Apo-α-LA is treated with Au3+, it results in the formation of a protein-coated Au10 nanocluster where the protein reduces Au3+ to Au0 and protects the nanoclusters (apo-α-LA-AuNCs) which are luminescent. In these protein-protected luminescent gold nanoclusters, the protein is involved both in reduction as well as protection, thereby supporting green synthesis. As La3+ occupies the Ca2+ site in apo-α-LA, the size of AuNCs formed is reduced to smaller than the Au10, where the size is dependent on the extent to which La3+ is bound to the protein with a concomitant increase in luminescence. The apo-α-LA-AuNCs and the same formed in the presence of different concentrations of La3+-bound protein were all characterized by analytical, spectral, and microscopy techniques. Control of the size of AuNCs formed was also studied by using Gd3+ instead of La3+ and found similar results. In particular, the size variation of AuNCs was clearly demonstrated by MALDI-TOF-MS and HRTEM. Thus, the apo-α-LA protein-coated gold nanocluster is a useful green material for suitable applications.
Go to article |
-
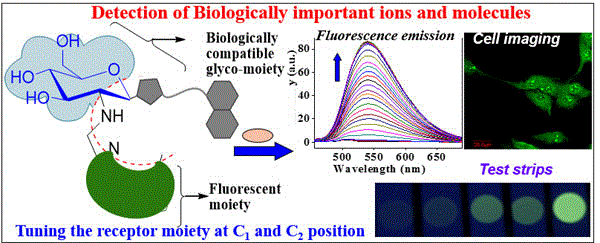 |
This perspective article prepared based on the doctoral thesis work of one of the authors mainly focuses to provide a comprehensive and comparative view of designing glucosyl-based molecular systems possessing binding cores to act as receptors for ions and molecules in solution and on solid surface and to provide cellular imaging in demonstrating their practical applicability.
Go to article |
-
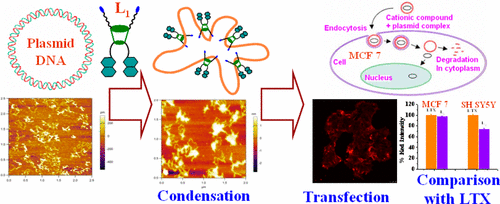 |
A new bimodal fluorescent cationic calix[4]arene (L1) conjugate has been synthesized in multiple steps and well characterized by NMR and electrospray ionization–mass spectrometry (ESI–MS) techniques. L1 has been investigated for its DNA binding ability by various spectroscopy techniques like absorption, fluorescence, and circular dichroism (CD). The formation of L1–DNA complex has been confirmed by the gel electrophoresis in the presence of incremental concentration of L1. To visualize the packing of the plasmid (pBR322), detailed tapping mode atomic force microscopy study has been performed, which revealed blob-like structure of plasmid upon addition of the incremental amount of L1. Concentration dependent transfection ability of L1 has been established in MCF-7 cells by confocal microscopy by carrying the red fluorescent protein (RFP) encoded plasmid pCMV-tdTomato-N1 to emit both intrinsic fluorescence of L1 as well as that from RFP. All this has been possible in the absence of any adjuvant phospholipids (DOPE) that are commonly used as helper. Further transfection efficiency of L1 has been compared with the commercially available lipofectamine (LTX) in two cancer cell lines, MCF 7 and SH-SY5Y, and found that the L1 is as efficient as that of LTX. Hence, L1 is an efficient and effective cargo to transport genetic material into the cells.
Go to article |
-
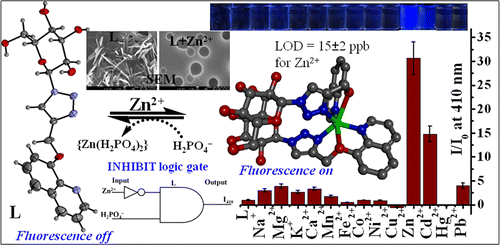 |
A water-soluble triazole-linked quinoline conjugate of glucopyranose (L) has been synthesized and characterized, and its single-crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) structure has been established. Binding of L toward different biologically relevant metal ions has been studied using fluorescence and absorption spectroscopy in HEPES buffer at pH 7.4. The conjugate L detects Zn2+ and Cd2+ with 30 ± 2 and 14 ± 1-fold fluorescence enhancement, respectively, but in the case of Hg2+, only a fluorescence quench was observed. The stoichiometry of the complex is 1:2 metal ion to the ligand in the case of Zn2+ and Cd2+ resulting in [Zn(L)2] and [Cd(L)2], and it is 1:1 in the case of Hg2+, as confirmed from their electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESIMS) spectra. Zn2+ shows greater exothermicity over Cd2+, whereas Hg2+ shows endothermicity , which supports the differences in their binding strength and the nature of the corresponding complex. L exhibits rod-shaped particles and upon complexation with Zn2+, it exhibits sphere-like morphological features in scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images. However, clustered aggregates are observed in Cd2+, whereas the [HgL] complex exhibits small fused spherical structures, and therefore the signature of these ions is seen in microscopy images. The computational studies revealed that the syn-[Zn(L)2] complex is stabilized by 9.7 kcal mol–1 more than that in the case of anti-[Zn(L)2] owing to the formation of hydrogen bonds between the two glucosyl moieties within the syn-complex. Among the anions studied, [Zn(L)2] is sensitive and selective toward the phosphate ion (H2PO4–) with a minimum detection limit of 16 ± 2 ppb. Similarly, the [HgL] can act as a secondary sensor for CN– while also exhibiting reversibility. Based on the input–output characteristics, INHIBIT logic gate was built in the case of Zn2+ vs H2PO4– and IMPLICATION logic gate was built in the case of Hg2+ vs CN–.
Go to article |
-
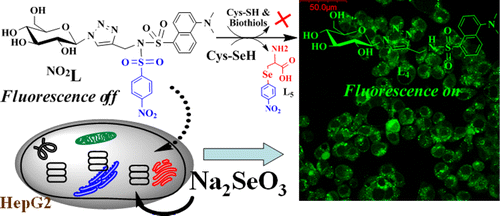 |
A dansyl derivatized triazole linked glucopyranosyl conjugate (NO2L) has been synthesized and characterized and was used in the present study. The conjugate NO2L releases a fluorescent product upon reaction by Cys-SeH in aqueous PBS buffer by exhibiting a ∼210-fold fluorescence enhancement even in the presence of 20 other amino acids with a minimum detection limit of (1.5 ± 0.2) × 10–7 M. The selectivity of the Cys-SeH to NO2L was further proven by extending the fluorescence study to different other selenium compounds. The role of para-nitrobenzenesulfonyl (pNBS) center in NO2L in the selective recognition of Cys-SeH was confirmed when the fluorescence emission studies were carried out using five different derivatizations possessing two NO2, five fluoro, two fluoro, one fluoro, and no fluoro groups. The nucleophilic substitution reaction of Cys-SeH on NO2L has been clearly demonstrated on the basis of 1H NMR, ESI-MS, and absorption spectroscopy, and the heat changes were monitored by isothermal titration calorimetry. The application potential of NO2L has been demonstrated by studying its selectivity toward Cys-SeH in aqueous PBS buffer, in bovine serum, and on the silica gel surface that lead to minimum detection limits of (25 ± 2), (80 ± 5), and (168 ± 16) ppb, respectively. The biological applicability of NO2L for Cys-SeH was further demonstrated in HepG2 cells by fluorescence microscopy. Thus, NO2L is aqueous soluble and a biologically acceptable probe for Cys-SeH.
Go to article |
-
 |
The development of probes for Hg2+ ion has been an active area of research in recent years because of the ill effects of this ion on the human health and environment. Hence the probe that needs to be developed should be sensitive as well as biologically compatible. This review mainly focuses to provide a comprehensive and comparative view of advances reported over the past ten years of literature, including our own contributions, in the design and application of the carbohydrate-based conjugates as fluorescent sensors for mercury. Therefore, this review covers aspects, such as, Hg2+ ion recognition, sensing and complexation by carbohydrate conjugates addressed using different spectral techniques and their critical analysis in a comparative manner.
Go to article |
-
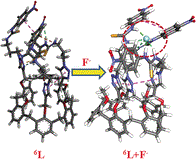 |
Anion recognition studies were performed with triazole-appended thiourea conjugates of calix[6]arene (i.e., compound 6L) by absorption and 1H NMR spectroscopy by using nineteen different anions. The composition of the species of recognition was derived from ESI mass spectrometry. The absorption spectra of compound 6L showed a new band at λ=455 nm in the presence of F− due to a charge transfer from the anion to the thiourea moiety and the absorbance increases almost linearly in the concentration range 5 to 200 μm. This is associated with a strong visual color change of the solution. Other anions, such as H2PO4− and HSO4−, exhibit a redshift of the λ=345 nm band and the spectral changes are associated with the formation of an isosbestic point at λ=343 nm. 1H NMR studies further confirm the binding of F− efficiently to the thiourea group among the halides by shifting the thiourea proton signals downfield followed by their disappearance after the addition of more than one equivalent of F−. The other anions also showed interactions with compound 6L, however, their binding strength follows the order F−>CO32−>H2PO4−≈CH3COO−>HSO4−. The NMR spectral changes clearly revealed the anion-binding region of the arms in case of all these anions. The anion binding to compound 6L indeed stabilizes a flattened-cone conformation as deduced based on the calix-aromatic proton signals and was further confirmed by VT 1H NMR experiments. The stabilization of the flattened-cone conformation was further augmented by the interaction of the butyl moiety of the nBu4N+ counterion. The structural features of the anion-bound species were demonstrated by DFT computations and the resultant structures carried the features that were predicted based on the 1H NMR spectroscopic measurements. In addition, SEM images showed a marigold flower-type morphology for compound 6L and this has been transformed into a chain-like structure of connected spherical particles in the presence of F−. The anion-induced microstructural features are reflective of the binding strength, size, and shape of the anions. The binding strengths of the anions by compound 6L were further compared with that of compound 4L, a calix[4]arene analogue of compound 6L, in order to address the role of the number of arms built on the calixarene platform based on absorption spectroscopy, 1H NMR spectroscopy, and DFT computations and it was found that compound 6L is a better receptor for F−, which extends its interactions from all the three arms.
Go to article |
-
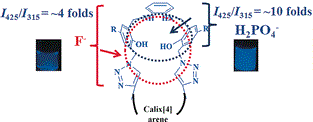 |
A phenylenediamine-capped conjugate of calix[4]arene (Lamino) was synthesized by reducing its precursor, Limino, with sodium borohydride in methanol. The Lamino sample binds to anions due to the more flexible and bent conformation of the capped aminophenolic binding core, compared to the precursor Limino. The Lamino sample showed selectivity towards H2PO4− by exhibiting a ratiometric increase in emission by about 11-fold with a detection limit of (1.2±0.2) μm ((116±20) ppb) over 15 anions studied, including other phosphates, such as P2O74−, adenosine monophosphate (AMP2−), adenosine diphosphate (ADP2−), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP2−). The Lamino sample shows an increase in the absorbance at λ=315 nm in the presence of H2PO4−, CO32−, HCO3−, CH3CO2−, and F−. The 1H NMR spectroscopic titration of Lamino with H2PO4−, F−, and CH3CO2− showed major changes in the phenylene-capped and salicyl moieties, and thereby, confirming the aminophenolic region as the binding core. However, the binding strength of these anions followed the trend H2PO4−>F−≫CH3CO2−>HSO4−. The heat changes observed by isothermal titration calorimetry support this trend. The Lamino sample showed reversible sensing towards H2PO4− and F− in the presence of Mg2+ and Ca2+, respectively. NOESY studies of Lamino, in comparison with its anionic complexes, revealed that major conformational changes occurred in the capping region to facilitate the binding of anion. ESI-MS and the Job's method revealed 1:1 stoichiometry between Lamino and H2PO4− or F−. In the SEM micrographs of Lamino, the spherical particles are converted into spherical aggregates and further form large agglomerates and even branched sheets in the presence of anions, depending upon their binding strength.
Go to article |
-
 |
A free Cys-SH-containing protein, β-lactoglobulin (β-LG), and another protein not possessing the same, viz., apo-α-lactoglobulin (apo-α-LA), were used in studies to demonstrate the role of this amino acid, along with its secondary structure, in the formation of a protein dimer and a protein–inorganic hybrid nanoflower and in the creation of the peroxidase-like activity of the nanomaterials produced when the proteins were treated with varying Cu2+ concentration under different pH conditions. An increase in the pH as well as the Cu2+ mole ratio results in increasing dimer formation in case of β-LG due to the presence of free Cys121-SH, while the dimer is not formed in case of apo-α-LA under the same conditions. The role of Cys in the dimer formation has been demonstrated both by MALDI and sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis studies. Both of the proteins exhibited changes in their secondary structures to different extents as a function of pH, and the structures were stabilized by Cu2+ interactions, as studied by CD and fluorescence spectroscopy. The small and spherical nanoparticles formed at pH 7 with lower equivalents of Cu2+ join together to form larger aggregates at higher equivalents of Cu2+. For the same concentration at pH 9, both the aggregates and the nanoflowers were noticed. However, at pH 12, the Cu2+ binding induces the formation of fibers along with the flowers. Both the nanoflowers and nanofibers exhibited peroxidase-like activity in a catalytic manner. Nanoflowers were also shown to detect phenol in the concentration range from 10 to 200 μM. The copper-induced nanobiomaterial obtained in the case of apo-α-LA also exhibited peroxidase-like activity. Thus, this paper deals with the green synthesis of copper-induced protein (β-LG/apo-α-LA)–inorganic hybrid nanomaterials that are important due to their applications as nanobiomaterials.
Go to article |
-
 |
A bifunctional calix[4]arene molecule bearing coumarin moiety on the lower rim and thioether moiety on the upper rim (L1), has been synthesized and well characterized by 1H, 13C NMR and mass spectrometry. Suitably functionalized coumarin moieties are well suited for selective recognition of various cations and anions. Among the 10 different metal ions studied, only Cu2+ and Fe3+ exhibit appreciable changes in the absorption spectra owing to the availability of functional moieties present at both the lower as well as the upper rim of free L1 in acetonitrile solution. To bring better selectivity, we blocked one of these functional moieties by coating on to a surface so that only the other one is exposed to the environment for sensing. Such a study carried out in the present case using the self-assembled monolayer (SAM) of L1 on Au(111) resulted in selective sensing of Cu2+ over several other metal ions as studied by surface plasmon resonance (SPR). The SAM of L1 on Au(111) was confirmed by different techniques, such as grazing incidence FT-IR, contact angle measurement, cyclic voltammetry and scanning tunneling microscopy. Thus, L1 is proven to be a suitable sensor for Cu2+ when attached to gold surface
Go to article |
-
 |
Dansyl-derivatized, triazole-linked, glucopyranosyl conjugates, 5FLOH, 2FLOH, 1FLOH, and 0FLOH were synthesized and characterized. While the 5FLOH acts as a molecular probe for CN–, 2FLOH, 1FLOH, and 0FLOH acts as control molecules. The reactivity of CN– toward 5FLOH has been elicited through the changes observed in NMR, ESI MS, emission, and absorption spectroscopy. The conjugate 5FLOH releases a fluorescent product upon reaction by CN– in aqueous acetonitrile medium by exhibiting an ~125-fold fluorescence enhancement even in the presence of other anions. Fluorescence switch-on behavior has been clearly demonstrated on the basis of the nucleophilic substitution reaction of CN– on 5FLOH. A minimum detection limit of (2.3 ± 0.3) × 10–7 M (6 ± 1 ppb) was shown by 5FLOH for CN– in solution. All the other anions studied showed no change in the fluorescence emission. The utility of 5FLOH has been demonstrated by showing its reactivity toward CN– on a thin layer of silica gel as well as on Whatman No. 1 cellulose filter paper strips. The role of glucose moiety and the penta-fluorobenzenesulfonyl reactive center present in 5FLOH in the selectivity of CN– over other anions has been demonstrated by fluorescence, absorption and thermodynamics study. Similar studies carried out with the control molecules showed no selectivity for CN–. The mechanistic aspects of the reactivity of CN– toward 5FLOH were supported by DFT computational study.
Go to article |
-
 |
A water-soluble glucopyranosyl conjugate, L, has been synthesized and characterized by different analytical anspectral techniques. The L has been demonstrated to have switch-on fluorescence enhancement of ~75 fold in the presence of La3+ among the nine lanthanide ions studied in the HEPES buffer at pH 7.4. A minimum detection limit of 140 nM (16 ± 2 ppb) was shown by L for La3+ in the buffer at physiological pH. The utility of L has been demonstrated by showing its sensitivity toward La3+ on Whatman filter paper strips. The reversible and reusable action of L has been demonstrated by monitoring the fluorescence changes as a function of the addition of La3+ followed by F– and HPO42– ions. The complexation of L by La3+ was shown by absorption spectra wherein isosbestic behavior was observed. The Job’s plot suggests a 2:1 complex between L and La3+, and the same was supported by ESI-MS. The control molecular study revealed the necessity of hydroxy quinoline and the amine group for La3+ ion binding and the glyco-moiety to bring water solubility and biocompatibility. The structural features of the [2L+La3+] complex were established by DFT computational calculations. The chemo-ensemble, [2L+La3+], is shown responsible for providing intracellular fluorescence imaging in HepG2 cells.
Go to article |
-
 |
A water soluble and biocompatible glucopyranosyl conjugate (L) has been synthesized and characterized by various techniques. The L has been employed to recognize Cys selectively among the naturally occurring amino acids in HEPES buffer at physiological pH. A minimum detection limit of 2.5 × 10-7 M was shown by L for Cys in the buffer at pH = 7.4. The reactivity of L towards biological thiols as demonstrated by emission and absorption is supported by the observed increase in the fluorescence intensity; however, Cys shows a maximum increase owing to its better nucleophilicity. The reactivity of Cys on L is demonstrated by 1H NMR, ESI MS, emission and absorption spectroscopy, and the formation of the binary complex was supported by ESI MS. The control molecular study revealed the necessity of the glyco-moiety to bring water solubility and biological adaptability. The cellular studies support that the conjugate L is biologically adaptable and shows effective intracellular fluorescence emission upon reacting with intracellular thiols.
Go to article |
-
 |
A phenylene diimine capped conjugate of 1,3-calix[4]arene (L) was synthesized and characterized, and its Mg2+ complex has been isolated and characterized. The chemo sensing ensemble of Mg2+ bound L provides distinguishable features of response toward phosphates, viz., HPO42–, P2O74–, and AMP2– (Set A) and H2PO4–, ATP2–, and ADP2– (Set B). While the Set A shows the formation of ternary complex, the Set B does not exhibit any intermediate complex, but both show the release of Mg2+ and L at different equivalents. The structures of {L + Mg2+} and its phosphate bound ternary complexes have been established by computational calculations, and the corresponding results agree well with the experimental ones. The microscopy studies show an aggregation–disaggregation phenomenon in the presence of different equivalents of phosphates in both of the sets. Using the fluorescence data, an INHIBIT logic gate has been built.
Go to article |
-
 |
Binding of Pb2+ to lentil lectin (LL) was studied by spectroscopy, microscopy and thermodynamics and the species were modelled by molecular dynamics (MD). The effect of pH on Pb2+ binding was studied at pH = 5 in acetate buffer and pH = 7.2 in Tris buffer. Based on ITC, multiple binding sites were found for Pb2+ at pH = 7.2. No binding is noticed at pH = 5. The MD results showed the involvement of aspartate and glutamate with hemi-directed geometry for Pb2+. Pb2+ mediated ß sheet to a-helix transition was noticed at pH = 7.2. At physiological pH, morphological changes were observed in the reduction of size of the particles of LL (160 ± 30 nm) to those in {LL + Pb2+} (45 ± 10 nm) as derived based on AFM and TEM. In presence of Pb2+, the larger particles break down to smaller ones because of the coordination ability of Pb2+ towards carboxylate and imidazole moieties. At pH = 5, the TEM shows much higher aggregation than that observed at pH = 7.2 for the protein alone, leading to linear aggregated species which were further broken down by Pb2+ into smaller ones.
Go to article |
-
 |
A new fluorescent 1,3-diaminonaphthalimide conjugate of calix[4]arene receptor (R) was synthesized and characterized. The receptor displays good selectivity towards trinitrophenol (TNP) over other explosive aromatic- and aliphatic-nitro compounds by exhibiting changes in its fluorescence emission. Receptor-coated cellulose paper strips are equally effective in terms of their selective detection of TNP over other aromatic- and aliphatic-nitro compounds. When used in solution or on cellulose paper strips, R can detect up to submicromolar concentration of TNP by exhibiting changes in its fluorescence emission and in its supramolecular structure upon interaction. Interestingly, the microscopy features of R, TNP, and {R+TNP} are quite distinct, indicating the interactions present between R and TNP, as studied by using AFM and TEM. Computationally modeled complexes of receptor with TNP and TNT show enormous difference in their interaction energies in the favor of TNP by showing the host–guest interaction of cation···anion type in the presence of TNP but not TNT. This is because the receptor adopts an “arms-open”-type structure in the case of the TNP complex, whereas it adopts an “arms-closed”-type structure in the presence of TNT. Both the experimental and the computational studies reveal that the receptor selectively binds to TNP over TNT. Thus, R-coated Whatman No.1 filter paper strips provide easy, rapid, and economical detection of trace amounts of TNP both by visual and spectral measurement.
Go to article |
-
 |
Gels are interesting soft materials owing to their functional properties leading to potential applications. This paper deals with the synthesis of monocholesteryl derivatized calix[4]arene (G) and its instantaneous gelation at a minimum gelator concentration of 0.6% in 1:1 v/v THF/acetonitrile. The gel shows remarkable thermoreversibility by exhibiting Tgel?sol at ~48 °C and is demonstrated for several cycles. The gel shows an organized network of nanobundles, while that of the sol shows spherical nanoaggregates in microscopy. A bundle with ~12 nm diameter possessing hydrophobic pockets in itself is obtained from computationally modeled gel, and hence the gel is suitable for storage and release applications. The guest-entrapped gels exhibit the same microstructures as that observed with simple gels, while fluorescence spectra and molecular mechanics suggests that the drug molecules occupy the hydrophobic pockets. All the entrapped drug molecules are released into water, suggesting a complete recovery of the trapped species. The reusability of the gel for the storage and release of the drug into water is demonstrated for four consecutive cycles, and hence the gel formed from G acts as a functional material that finds application in drug delivery.
Go to article |
-
 |
Lower rim amide linked 8-amino quinoline and 8-amino naphthalene moiety 1,3,5-triderivatives of calix[6]arene L1 and L2 have been synthesized and characterized. While the L1 acts as a receptor molecule, the L2 acts as a control molecule. The complexation between L1 and Cu2+ or Zn2+ was delineated by the absorption and electrospray ionization (ESI) MS spectra. The binding ability of these molecules toward biologically important metal ions was studied by fluorescence and absorption spectroscopy. The derivative L1 detects Zn2+ by bringing ratiometric change in the fluorescence signals at 390 and 490 nm, but in the case of Cu2+, it is only the fluorescence quenching of 390 nm band that is observed, while no new band is observed at 390 nm. The stoichiometry of both the complexes is 1:1 and was confirmed in both the cases by measuring the ESI mass spectra. The isotopic peak pattern observed in the ESI MS confirmed the presence of Zn2+ or Cu2+ present in the corresponding complex formed with L1. Among these two ions, the Cu2+ exhibits higher sensitivity. The density-functional theory (DFT) studies revealed the conformational changes in the arms and also revealed the coordination features in the case of the metal complexes. The arm conformational changes upon Zn2+ binding were supported by nuclear Overhauser effect spectrometry (NOESY) studies. The stronger binding of Cu2+ over that of Zn2+ observed from the absorption study was further supported by the complexational energies computed from the computational data. While the L1 exhibited spherical particles, upon complexation with Cu2+, it exhibits chain like morphological features in scanning electron microscopy (SEM) but only small aggregates in the case of Zn2+. Thus, even the microscopy data can differentiate the complex formed between L1 and Cu2+ from that formed with Zn2+.
Go to article |
-
 |
A green synthesis was developed in order to prepare protein coated gold nanoparticles using a metal free, a-helical protein, i.e., apo-a-LA, that acts as both the reducing as well as stabilizing agent to result in Au0 nanoparticles from Au3+ which are luminescent and hence can be used for biological imaging, including of cells. The nanoparticles, apo-a-LA-AuNPs, thus synthesized were characterized by multiple techniques, such as, analytical, spectral, microscopy and light scattering, in order to support the presence of NPs in terms of their size and shape, involvement of Au0 and the protein encapsulation and its structural changes upon coating. The 10–16 nm sized apo-a-LA-AuNPs were shown to be non-toxic to healthy cells as studied using normal mouse fibroblast cells (L929). Having found that these NPs are biocompatible and possess structurally altered apo-a-LA protein, the luminescent apo-a-LA-AuNPs were demonstrated to have cytotoxicity towards cancer cells as studied by cell viability tests as well as fluorescence microscopy. While these NPs kill ~75% of MCF-7 cells, at the same concentration these are capable of killing only ~30% of HeLa cells, thus exhibiting cell dependency. The present study clearly demonstrates the advantage of the luminescent apo-a-LA-AuNPs in their attack of cancer cells in general and selective killing of breast cancer cells in particular. Thus coating AuNPs with the protein apo-a-LA enhanced their anticancer activity several fold.
Go to article |
-
 |
A coumarine–imino–C2-glucosyl conjugate (L) was synthesized and characterized. The conjugate L is found to recognize Cu2+ in aqueous HEPES buffer by exhibiting a 95% fluorescence quenching in pH range 7–10 even in the presence of several biologically and ecologically relevant metal ions. Fluorescence on–off behavior has been clearly demonstrated on the basis of the binding variability of Cu2+ to L. The binding has been elicited through the changes observed in fluorescence, absorption, ESI-MS and 1H NMR titrations. All the other thirteen metal ions studied did not show any change in the fluorescence emission. These ions do not interfere with the recognition of Cu2+ by L. The structural features of [CuL]2 complex in both the isomeric forms were established by DFT computational calculations. The utility of L has been demonstrated by showing its sensitivity toward Cu2+ on a thin layer of silica gel. The L gives sensitive fluorescence signals for Cu2+ even in blood serum and exhibits appropriate fluorescence responses in living cells.
Go to article |
-
 |
Self assembly of biomolecules is important not only in unravelling the fundamental aspects of biology but also in exhibiting their supramolecular structures wherein the self assembly acts as a basic principle. Therefore, proteins having different side chains and structures with varying binding affinities towards metal ions can certainly be manifested in generating myriad supramolecular structures. In order to demonstrate this, we have chosen several ß-sheet lectins, such as, Horse gram lectin (DBL), Pisum sativum agglutinin (PSA), Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA), Allium sativum agglutinin also known as garlic lectin (ASA) and Concanavalin A (Con A) lectin, in conjunction with Zn2+ and Cu2+ as biologically important ions and showed that these form nanostructures, such as, open-, rolled- and stacked sheets, and tubes. The Zn2+ induces mainly the sheets in the lectins studied so far though some of these are thin and others are thick, while some are folded and others are not. However, Cu2+ induces mainly tubes in ASA and DBL, predominantly sheets in Con A and a mixture of tubes and sheets in PSA and WGA as shown by TEM and supported by SEM. The tubes formed were thick as well as thin, solid as well as hollow in nature, straight, cylindrical as well as twisted and ribbon shaped. Plasmid PBR322 treated nanostructures formed from PSA in the presence of Cu2+ showed the presence of the plasmid in the corresponding tubes and sheets. These nanostructures are unprecedented and could lead to major advances in biomaterials science by providing potential applications.
Go to article |
-
 |
A triazole-linked hydroxyethylimino conjugate of calix[4]arene (L) and its cadmium complex have been synthesized and characterized, and their structures have been established. In the complex, both the Cd2+ centers are bound by an N2O4 core, and one of it is a distorted octahedral, whereas the other is a trigonal anti-prism. The fluorescence intensity of the di-nuclear Cd(II) complex is quenched only in the presence of phosphates and not with other anions studied owing to their binding affinities and the nature of the interaction of the phosphates with Cd2+. These are evident even from their absorption spectra. Different phosphates exhibit changes in both their fluorescence as well as absorption spectra to varying extents, suggesting their differential interactions. Among the six phosphates, H2PO4- has higher fluorescence quenching even at low equivalents of this ion, whereas P2O74- shows only 50% quenching even at 10 equivalents. The fluorescence quenching is considerable even at 20 ppb (0.2 µM) of H2PO4-, whereas all other phosphates require a concentration of 50–580 ppb to exhibit the same effect on fluorescence spectra. Thus, the interaction of H2PO4- is more effective by ~30 fold as compared to that of P2O74-. Fluorescence quenching by phosphate is due to the release of L from its original cadmium complex via the formation of a ternary species followed by the capture of Cd2+ by the phosphate, as delineated based on the combination of spectral techniques, such as absorption, emission, 1H NMR and ESI MS. The relative interactive abilities of the six phosphates differ from each other. The removal of Cd2+ is demonstrated to be reversible by the repeated addition of the phosphate followed by Cd2+. The characteristics of the ternary species formed in each of these six phosphates have been computationally modeled using molecular mechanics. The computational study revealed that the coordination between cadmium and –CH2–CH2–OH breaks and new coordination is established through the phosphate oxygens, and as a result the Cd2+ center acquires a distorted octahedral geometry. The utility of the complex was demonstrated in HeLa cells.
Go to article |
-
 |
Herein we report the synthesis and characterization of 7-oxanorbornadiene (OND)-appended 1,3,5-tris conjugate of calix[6]arene (L2). L2 has been shown to exhibit selective reactivity toward cysteine (Cys) over homocysteine (Hcy) and glutathione (GSH) under stoichiometric conditions. The selectivity of L2 is attributed to the steric crowding of three Diels–Alder centers possessing OND units present on the calix[6]arene platform, while a control molecular system possessing only one such unit without the calix[6]arene platform (L1) does not show any selectivity toward Cys. While L2 exhibited spherical particles, its reactivity with Cys resulted in flowerlike morphological features, as revealed by scanning electron microscopy. However, the reaction with GSH did not result in any such morphological features, a result that is in agreement with that observed from fluorescence studies in solution. L2 has been shown to react with Cys present in HeLa and Jurkat E6 cells by fluorescence microscopy.
Go to article |
-
 |
Nanoparticles and nanocrystals of mercury are formed when Hg2+ salt reacts with apo-a-lactalbumin (apo-a-LA). Reduction followed by nanoparticle formation is further augmented by the protein, as it also acts as a coating agent. The initial interaction of Hg2+ with apo-a-LA was demonstrated by changes observed in absorption, emission, and CD spectroscopy, where the latter technique also detected structural changes in the protein. Such structural changes are expected when Hg2+ binds to the protein, and therefore, the binding was determined by isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC). The binding was further proven by MALDI, which showed mercurated species of protein with a Gaussian distribution exhibiting a weighted average of 6 and 9 Hg2+ ions bound to protein when apo-a-LA was treated with 10 and 100 equivalents, respectively. The molecular dynamics studies revealed the binding of Hg2+ ions followed by the structural changes that occurred in the protein. The reaction between Hg2+ and apo-a-LA yields non-crystalline nanoparticles at lower molar ratios of Hg2+ and crystalline ones at higher molar ratios. The existence of both of these nanoparticles was proven by extensive TEM studies, and the mercury nanocrystals were further studied using fluorescence microscopy. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy demonstrated that the protein has the ability to convert Hg2+ to Hg0, and the resultant Hg0 cluster is known to be less harmful than Hg2+ to the organism. All of these studies support the use of apo-a-LA in the form of nanoparticles and nanocrystals to detoxify Hg2+.
Go to article |
-
 |
A broad spectrum of peptides and proteins can self assemble to form amyloid or amyloid like fibrils under appropriate conditions. Although amyloid fibrils have recently been exploited for their potential use as biomaterials, their applications remain challenging. In this paper, we have shown the formation of amyloid like fibrils of peanut agglutinin isolated from leguminacea class that is rich in beta sheet secondary structure under thermal conditions in the presence of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Cu2+. Formation of such fibrils has been followed and also assayed by different spectroscopy techniques. This was further evaluated by transmission electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy and scanning electron microscopy revealing their morphological features at the nano-scale. The blue-green fluorescence of these fibrils treated with dansyl chloride was micrographed. The role of these metal ions has been revealed by carrying out the experiments in the presence of EDTA that chelates these metal ions. Furthermore, the Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis clearly showed that the fibrils are enriched with these metal ions. During the formation of fibrils, the presence of granular, sponge-like, network-like and proto-filaments has been witnessed. In order to demonstrate the utility of such self assembled fibrils induced by metal ions, these were shown to bind and possess circular – PBR322 plasmid, and hence are expected to have potential applications in gene delivery and related therapy.
Go to article |
-
 |
A triazolium-anthracenyl calix[4]arene conjugate (L) was synthesized by methylating the precursor triazole derivative and then characterized. The potential of the cationic L to differentiate nucleoside triphosphates (NTPs) from their mono- and diphosphates was demonstrated. Due to its unique combination of arms with the calix-platform, a fluorescence enhancement was observed for L with all the NTPs, whereas there is no report with such enhancement being exhibited in case of all the NTPs. This has been supported by the aggregation of L observed from microscopy. Selectivity of L towards NTPs over other phosphates was a result of specific weak interactions, namely, ion–ion, hydrogen bonding and p···p, present in the 1:2 complex of L and NTPs (based on ESI MS), which were absent in their congener-phosphates as delineated by NMR and computational studies. Thus, L stands as a unique receptor for NTPs.
Go to article |
-
 |
A pyrenyl-imino-C2-glucosyl conjugate, L, has been synthesized and characterized. The L exhibits selective chromogenic as well as fluorescent property towards Hg2+ in a ratiometric manner by showing ~30 fold enhanced fluorescence emission intensity. The fluorescence enhancement continues to be there even in the presence of thirteen other competitive metal ions studied. The sensing of Hg2+ is well demonstrated using various techniques, such as, fluorescence, absorption, visual color under UV light and ESI MS. A minimum detection limit of 18 ± 2 ppb was shown by L for Hg2+ in ethanol. All the experimental studies carried out supported the formation of 2:1 complex between L and Hg2+. The structure of the 2:1 complex was modeled at ab initio using HF and found a structure where Hg2+ is sandwiched between the two pyrenyl moieties. The reversibility and reusability of L has been demonstrated using fluoride ion.
Go to article |
-
 |
A phenylene-diimine-capped conjugate of lower rim 1,3-calix[4]arene (L) was synthesized, characterized, and shown to selectively bind to Mg2+ using its capped arms. This results in a selective recognition of Mg2+ through eliciting fluorescence enhancement of ~70 fold with a detection limit of 40 ± 5 ppb. However, in the presence of blood serum, the lowest detection limit is 209 ± 10 ppb (0.2 µM). The binding of Mg2+ to L is authenticated by absorption and 1H NMR data. The Job’s plot derived on the basis of the absorption data showed 1:1 stoichiometry between the receptor and Mg2+. The 1:1 species was further confirmed through ESI MS, that is, being supported by the isotope peak pattern authenticating the presence of Mg2+ in the complex. The L binds Mg2+ octahedrally using the tetradentate L2– and two additional acetic acid moieties by bringing conformational changes as studied on the basis of MM computations. The conformational changes that occur in the capped arms upon Mg2+ binding were supported experimentally by NOESY. AFM and SEM studies showed that spherical particles of L are modified into flower and chain type aggregates upon complexation with Mg2+, confirming the supramolecular behavior of the species formed.
Go to article |
-
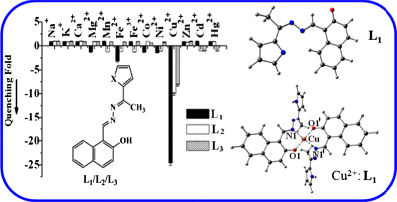 |
2-Hydroxynaphthylidene derivatives of hydrazine, namely L1, L2 and L3, were synthesized by going through two-step reactions and the products were characterized. The ion recognition properties of these receptors were studied using fluorescence and absorption spectroscopy. The receptors were found to be sensitive and selective towards Cu2+ in methanol solution among the 13 metal ions studied, namely Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, Pb2+, Na+, K+, Ca2+ and Mg2+, by exhibiting switch off fluorescence. The stoichiometry of the complexed species was found to be 2:1. The fluorescence quenching with Cu2+ is in the order of L1 > L2 > L3. These conjugates were also found to act as colorimetric sensors for Cu2+ in solution by exhibiting visual colour change. The 2:1 complex shows a centrosymmetric structure based on DFT computations.
Go to article |
-
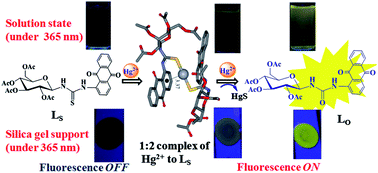 |
The glyco-conjugate, LS, its Hg2+ complex, and the LO were synthesized and characterized in their solid state by FTIR, diffuse reflectance, and powder XRD. The mercury complex shows dumbbell-like microstructures as a result of the metal ion-induced aggregation of the glyco-conjugate as studied based on scanning electron microscopy. The aggregation was also supported by atomic force microscopy. The Hg2+ was detected on LS-coated silica gel sheets by switch-on fluorescence, wherein, the enhancement in the fluorescence intensity varies linearly with the added Hg2+ in the concentration range 5–60 µM. The concentration-dependent variation was also detected on silica gel sheets by viewing their colour under 365 nm light. Hg2+ was detected by the LS-coated silica gel sheets by switch-on fluorescence even in the presence of blood serum. Thus, this method is extendable for the detection and quantification of Hg2+ present in blood and or in biological fluids using disposable silica gel sheets. The sensing of Hg2+ in HEPES buffer solution is well demonstrated in this paper using various techniques, such as fluorescence, absorption, visual color, ESI MS, and 1H NMR. In the buffer medium, the LS exhibit selective chromogenic as well as fluorogenic properties towards Hg2+ by showing ~75-fold higher fluorescence emission intensity and the studies were further extended to show that none of the 13 ions studied compete for Hg2+. A minimum detection limit of 25 ± 4 ppb was shown by LS for Hg2+ in the buffer. All the experimental studies carried out support the formation of 2 : 1 complex between LS and Hg2+. At higher mole ratios of Hg2+, the same yields the oxo-product, viz., LO. The structure of the 2 : 1 complex was modeled by DFT using B3LYP/LANL2DZ.
Go to article |
-
 |
This paper deals with the development of a receptor with selectively functionalized at the lower rim of p-tert-butyl calix[4]arene linked through amide bond, resulting in the diamide derivatives (L1, L2 and L3) suitable for sensing ions and molecules. All the derivatives were thoroughly characterized by analytical and spectral methods. These derivatives were structurally characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction and the conformational features of the calix[4]arene as well as the pendants are discussed. The L1 and L2 exhibited intramolecular hydrogen bond interaction between the N–H and the lower rim phenolic oxygen in addition to the circular hydrogen bonding between the phenolic O–H and the ether oxygen of the adjacent strand. The corresponding H-bond is absent when no ‘H’ is present on amide-N as in case of L3. Such intramolecular N–H···O interactions observed with the pendant results in a conformational bend responsible for the orientation of the arms and there by the nature of the binding core formed. Thus the binding cores formed differ largely between L3 and the other two.
Go to article |
-
 |
A triethylene glycol di-imine locked triazole linked bis-calix[4]arene conjugate L has been synthesised and characterised. Conjugate L exhibits high fluorescence enhancement towards Zn2+ among the 13 metal ions studied down to a lower detection limit of ~12 ppb. The absorption and visual colour change experiments differentiated the Zn2+ from the other metal ions studied. The isolated zinc complex, [Zn2L] has been used as a chemo-sensing ensemble for the recognition of anions based on their binding affinities towards Zn2+. [Zn2L] was found to be sensitive and selective towards phosphate-bearing species and in particular to adenosine triphosphate (ATP2 - ) among the other 20 anions studied as observed based on the changes occurred in the fluorescence intensity. The selectivity of the ATP2 - has been shown on the basis of the changes observed in the emission and absorption spectral studies. The lowest detectable concentration for ATP2 - with the chemo-sensing ensemble [Zn2L] is 348 ppb in methanol. The fluorescence quenching by the phosphate-based anions has been modelled by molecular mechanics studies and found that the anions possessing two or more phosphate moieties can only bridge between the two zinc centres, and hence those possessing only one phosphate moiety (H2PO4- and AMP2 - ) are ineffective.
Go to article |
-
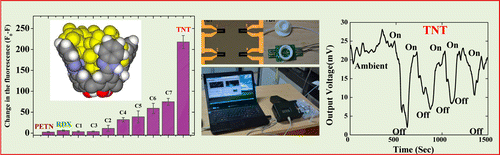 |
A new benzimidazole-functionalized calix[4]arene receptor (R) was synthesized and characterized. The receptor R shows better selectivity toward trinitrotoluene (TNT) compared to the other nitro explosives in solution, which also retains its effectiveness for solid-phase detection. The chemical interactions of the molecule with different nitro explosive analytes were studied by fluorescence spectroscopy and by a molecular dynamics approach. The molecular dynamics studies show a 1:3 complex between R and TNT, and hence high sensitivity was imparted by fluorescence studies. The detection of explosive vapors in ambient conditions was tested by using a sensitive coating layer of R on an SU-8/CB-based piezoresistive cantilever surface. The developed device showed large sensitivity toward TNT compared to cyclotrimethylenetrinitramine (RDX) and pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN) in the solid state at their respective vapor pressures at room temperature. The detection sensitivity of the device was estimated to be 35 mV for TNT at ambient conditions. Moreover, the sensor does not show a response when exposed to humidity.
These results demonstrate that R can be used as one of the coating materials for a cantilever for the detection of TNT using piezoresistivity measurement. R can also detect the explosives in solution with high sensitivity and selectivity by fluorescence spectroscopy.
Go to article |
-
 |
An amido-linked rhodamine conjugate of calix[4]arene, L has been synthesized and characterized. Metal ion recognition properties of L have been studied by emission and absorption techniques with 14 different metal ions including the transition ones. Results show that, L exhibits ratiometric emission intensity towards Hg2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Cu2+, Pb2+ and Zn2+. Composition of the complex formed in the solution has been found to be 1:2 (L:Mn?+?), based on the Job’s plot. The L can also act as a chemosensor for Hg2+ through naked eye detection. Fluorescence quenching observed at 485 nm follows an order, Hg2+?>?> Fe3+ ~ Cu2+?> Zn2+?> Pb2+?> Ca2+, while the enhancement observed at 580 nm follows, Hg2+?>?> Fe2+ ~ Pb2+?> Zn2+. Mode of interaction of Mn?+? with L is by the ring opening of spirolactam moiety.
Go to article |
-
 |
A simple colorimetric approach for Cu2+ sensing was developed on a diimino conjugate of glucosyl-cresol (L). The L is characterized by 1H-NMR and ESI-MS spectra. L exhibits intense greenish fluorescent color in ethanol. This highly fluorescing L has been used to recognize Cu2+ selectively among the ten biologically important metal ions studied. Secondary recognition of L as its complex of Cu2+ towards cysteine and histidine has been established among twenty naturally occurring amino acids studied. Thus, the sensing of Cu2+ by L, as well as its Cu2+ complex towards amino acids has been demonstrated by absorption and visual color change experiments. Both the absorption and colorimetric titration results suggest that compound L is a highly selective sensor for Cu2+ and its complex for cysteine and histidine.
Go to article |
-
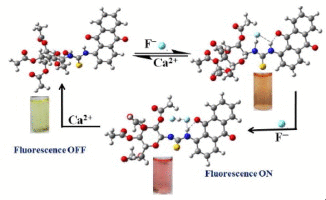 |
A new thiourea linked peracetylated glucopyranosyl–anthraquinone conjugate (L) has been synthesized and characterized. The binding properties of L have been studied with nineteen different anions. The L exhibited selective chromogenic as well as fluorescent chemosensor property toward F- by a ~13-fold increase in the emission intensity upon binding with F-. The minimal detection limit for F- is 185 ± 5 ppb in acetonitrile. Interaction of F- led to a bathochromic shift of 80 nm in the absorption band. An INHIBIT logic gate has been proposed using the output obtained from the fluorescence studies. The structure of the species formed upon the interaction of F- with L has been established by DFT computations.
Go to article |
-
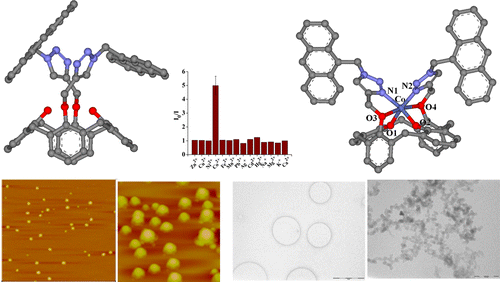 |
A new triazole-linked anthracenyl-appended calix[4]arene-1,3-diconjugate (L) has been synthesized and characterized, and its single crystal XRD structure has been established. Binding properties of L toward different biologically relevant metal ions have been studied by fluorescence and absorption spectroscopy in ethanol. L exhibits selective recognition of Co2+ and can detect down to a concentration of 55 ppb (0.92 µM). The roles of the calix[4]arene platform as well as the preorganized binding core in L’s selective recognition have been demonstrated by studying appropriate control molecules. The mode of binding of L with Co2+ has been modeled both by DFT and MD computational calculations. L and its Co2+ complex could be differentiated on the basis of the nanostructural features observed in AFM and TEM.
Go to article |
-
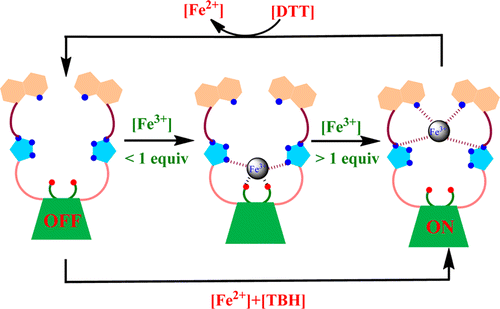 |
The synthesis and characterization of a triazole linked quinoline appended calix[4]arene conjugate, L, and its fluorescence turn on receptor property for Fe3+ have been demonstrated. The selective and sensitive discrimination of Fe3+ has been shown using fluorescence and absorption titration experiments. The Fe3+ binding to L has been further shown by ITC and ESI MS. The mode of binding of Fe3+ by calix[4]arene conjugate has been shown by absorption, 1H NMR and visual color change and the species were modeled based on DFT computations. The {L + Fe3+} has been shown to label cells with fluorescence imaging. Moreover the utility of this conjugate has been demonstrated by the combination logic gate system.
Go to article |
-
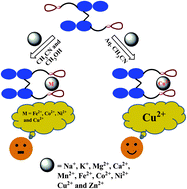 |
Di-amido-derivatives of 1,1'-methylene-bis(2-naphthol) (mbn), viz.; L1 to L6 and L7, have been synthesized and characterized. The single crystal X-ray structure of L2 has been established. All these derivatives have been studied for metal ion recognition by fluorescence and absorption techniques. Among these, L6 and L7 were found to be selective towards Cu2+ even in the presence of other metal ions in aqueous acetonitrile owing to the presence of the N,O-binding core up to the lowest concentration of 210 ± 11 and 144 ± 3 ppb, respectively. The binding region has been identified by 1H NMR studies. The proposed mode of binding has been modelled by DFT computations.
Go to article |
-
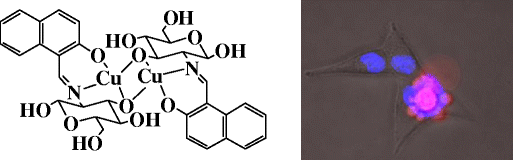 |
Binding of metal complexes of C2-glucosyl conjugates with DNA has been established by absorption and fluorescence studies. Conformational changes occurred in DNA upon binding have been studied by circular dichroism. All these studies are suggestive that the metal complexes bind to DNA through intercalation. Binding of di-nuclear copper complex 5 was found to be stronger when compared to the other complexes studied. Copper complexes were found to cleave the plasmid DNA in the absence of oxidizing or reducing agent, whereas, zinc complexes do not cleave. Metal complexes have shown toxicity to the HeLa and MCF–7 cell lines. Morphological studies, western blot and FACS analysis are suggestive of apoptotic cell death induced by the metal complexes. Di-nuclear copper complexes were found to be better as compared to the mononuclear ones in binding, plasmid cleavage and also in causing more cell death.
Go to article |
-
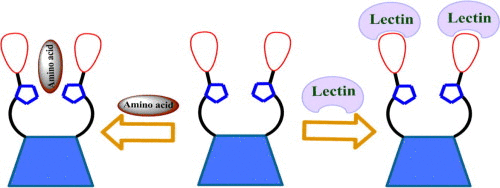 |
Triazole linked lower rim galactosyl and lactosyl appended calix[4]arene conjugates have been synthesized by 1,3 dipolar addition of glycosyl azide and calix[4]arene alkyne. All these conjugates were characterized by 1H and 13C NMR, IR and mass spectrometry. Interaction of amino acids with the galactosyl conjugate of calix[4]arene (5) was studied using absorption and 1H NMR techniques. Absorption studies showed that Trp interacts with triazole ring of 5. This was further confirmed by 1H NMR study which showed an upfield shift in the triazole proton of 5 upon titrating with Trp. The preliminary studies of interaction of these conjugates with Jacalin were demonstrated by fluorescence and circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy techniques.
Go to article |
-
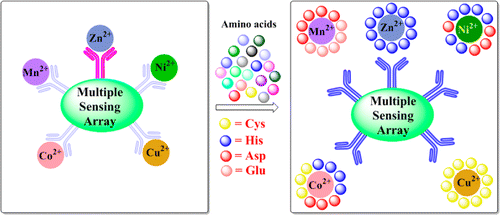 |
The triazole linked o-imino phenol appended calix[4]arene conjugate (L) has been synthesized and characterized. The structure of L has been established based on single crystal XRD. The binding and recognition behavior of conjugate, L toward the transition metal ions, such as Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+, has been demonstrated using fluorescence, absorption and ESI-MS techniques. The in situ prepared complexes of these metal ions, namely, [Mn2L], [Fe2L], [Co2L], [Ni2L], [Cu2L], and [Zn2L] have shown recognition toward Glu, Asp, His and Cys. Hence L provides a multiple sensing molecular tool where the response for the recognition of biologically active amino acids of metalloproteins is elicited by the presence of specific metal ion.
Go to article |
-
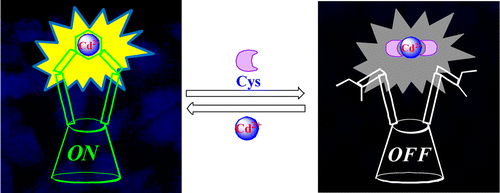 |
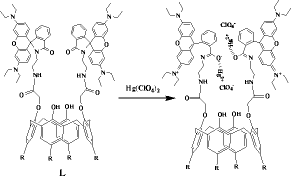
An N,N-Dimethylamine ethylimino-appended triazole-linked calix[4]arene conjugate, L, has been synthesized and characterized, and its Cd2+ complex has been isolated and characterized. The structure of [CdL] was established by computational calculation using B3LYP/LANL2DZ. Time-dependent density functional theory calculations were performed to demonstrate the electronic properties of [CdL]. This highly fluorescing [CdL] has been used to recognize Cys selectively among the 20 naturally occurring amino acids. [CdL] exhibits a minimum detection limit of 58 ppb for Cys, with reusability and reversibility being imparted to the system during sensing. Thus, the sensing of Cys was well demonstrated using various techniques, viz., fluorescence, absorption, visual color change, electrospray ionization MS, 1H NMR, and live cell imaging experiments.
Go to article |
-
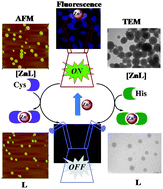 |
A highly fluorescent Zn2+ complex of the triazole linked salicyl-imino-thiophenyl conjugate of calix[4]arene, [ZnL] has been demonstrated to be a chemo-sensing ensemble for the recognition of His and Cys among the naturally occurring amino acids in HEPES buffer milieu. The recognition behaviour of the [ZnL] towards these amino acids has been shown on the basis of fluorescence, absorption and visual fluorescent colour changes. The species of recognition were shown by ESI MS titrations, AFM & TEM microscopy and cell studies.
Go to article |
-
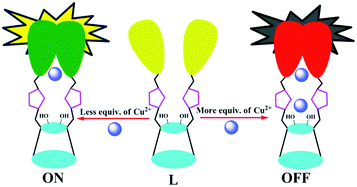 |
A benzimidazole appended triazole linked 1,3-diconjugate of calix[4]arene (L) has been synthesized and characterized. The conjugate L has been found to recognize Cu2+ among the thirteen different metal ions studied by exhibiting ratiometric fluorescence changes through newly generated excimer band at ~380 nm. Fluorescence off–on–off behavior has been clearly demonstrated on the basis of the binding variability of Cu2+ to L. The binding has been elicited through the changes observed in the fluorescence, ESI MS and 1H NMR titrations. All the other metal ions studied do not show any new band and further do not interfere with the recognition of Cu2+ by L, even when these are present in the same medium. The structural features of both the mono- and di-nuclear complexes were established by DFT computational calculations and found to display highly distorted geometry about the copper centers that deviate from both the tetrahedral and the square planar.
Go to article |
-
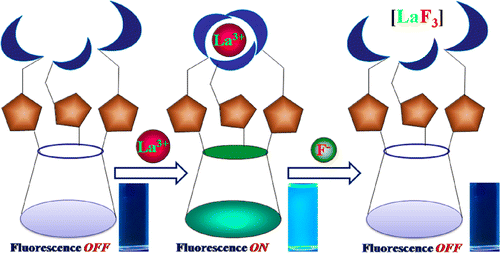 |
A new 1,3,5-tris-triazole linked picolylimine conjugate of calix[6]arene (L) has been shown to be selective toward La3+ by turn on fluorescence with ~70-fold enhancement and emits blue, with a minimal detection limit of 65 ± 5 ppb (490 nM). The species of recognition has been modeled computationally to have a monocapped twisted square antiprism with a N6O3 binding core about La3+. The in situ complex of L with La3+ recognizes F– via fluorescence quenching. The reversible response of sensing La3+ and F– sequentially by L has been demonstrated.
Go to article |
-
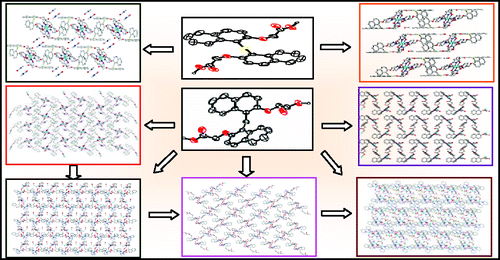 |
A series of five new Cu2+ coordination polymers, namely, {[CuLCH2(DMF)](DMF)}n (1), {[CuLCH2(DMF)(2,2'-bipy)](CH3OH)}n (2), {[CuLCH2(2,2'-bipy)](2H2O)}n (3), {[CuLCH2(H2O)(2,2'-bipy)](2H2O)}n (5), {[Cu2(LS)2(DMF)2](DMF)(CH3OH)(2H2O)}n (6), and three discrete coordination complexes {[Cu2LCH2(2,2'-bipy)2(CH3O)](ClO4)(CH3OH)} (4), {[CuLS(2,2'bipy)](CH3OH)} (7), and {[CuLS(1,10-phen)](DMF)} (8) have been prepared by the reaction of Cu(ClO4)2·6H2O and 1,1'-methylene-bis(2-naphthoxy acetic acid) (LCH2) or 1,1'-thio-bis(2-naphthoxy acetic acid) (LS), with or without the presence of 2,2'-bipyridine, under varying reaction conditions or methods of crystallization or both. All the compounds were characterized by elemental analysis, IR, thermogravimetric analysis, and single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD). The structures of LCH2 and LS obtained by single crystal XRD indicated anti- orientation of the pendant arms which upon metal complexation may turn into cis- orientation leading to discrete metal ion complexes or may remain in anti- orientation leading to extended multidimensional co-ordination polymers. The complexation with Cu2+ led to five different coordination spheres which in turn resulted in five different lattice structures. Thus, the present paper demonstrates the design of coordination polymers that are rich with mononuclear as well as dinuclear Cu2+ centers wherein LCH2 or LS coordinates in a monodentate as well as a bridging fashion leading to the formation of one-dimensional curving, helical, and two-dimensional networks.
Go to article |
-
-
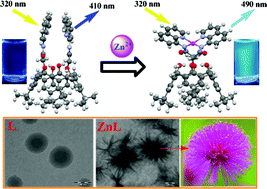 |
Carboxamidoquinoline appended calix[4]arene-1,3-di-conjugate (L) has been synthesized and characterized and its single crystal XRD structure has been established. L has been shown to act as selective ratiometric turn-on fluorescence sensor for Zn2+ up to a lowest concentration of 183 ± 18 ppb (2.82 µM) with a nine-fold enhancement by exhibiting blue-green emission. The coordination features of the species of recognition have been computationally evaluated by DFT methods and found to have distorted tetrahedral Zn2+ center in an N4 core. The spherical nano-structural features observed for L in TEM are being transformed into the Koosh nano-flower like structure when complexed with Zn2+ and hence these two can be easily differentiated. Even the features observed in AFM can distinctly differentiate L from its Zn2+ complex.
Go to article |
-
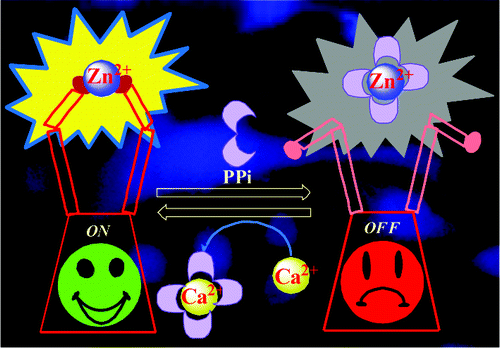 |
An in situ prepared Zn2+ complex of triazole linked imino-thiophenyl conjugate of calix[4]arene, [ZnL], was demonstrated to be highly fluorescent in HEPES buffer solution. [ZnL] has been used as a chemo-sensing ensemble for the recognition of phosphates in general and pyrophosphates in particular among the eighteen different anions studied. The chemo-sensing behavior of the [ZnL] has been demonstrated through fluorescence, absorption, visual fluorescent color changes, ESI MS, and 1H NMR titrations. Variations in the microstructural features of L, its zinc complex and the complex upon addition of PPi have been demonstrated through atomic force microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Such studies have been extended to see the permeability of the conjugate into the HeLa cells by fluorescence microscopy. In accession, a reversible “write-read-erase-read” logic gate property of L has been demonstrated through a feedback loop in the presence of Zn2+ and PPi.
Go to article |
- J. Dessingou, A. Mitra, K. Tabbasum, G. S. Baghel and C. P. Rao,
"Benzimidazole Conjugate of 1,1'-Thiobis(2-naphthol) as Switch-On
Fluorescence Receptor for Ag+ and the Complex as Secondary Recognition
Ensemble toward Cys, Asp, and Glu in Aqueous Methanolic Solution:
Synthesis, Characterization, Ion and Amino Acid Recognition,
Computational Studies, and Microscopy Features",
J. Org. Chem., 77(2012) 371-378, DOI:10.1021/jo201926q
- J. Dessingou, K. Tabbasum, A. Mitra, V. K. Hinge and C. P. Rao,
"Lower Rim 1,3-Di{4-antipyrine}amide Conjugate of Calix[4]arene:
Synthesis, Characterization, and Selective Recognition of Hg2+and Its
Sensitivity toward Pyrimidine Bases",
J. Org. Chem., 77(2012) 1406-1413, DOI:10.1021/jo2022372
- R. K. Pathak, V. K. Hinge, A. Rai, D. Panda, and C. P. Rao,
"Imino-phenolic-pyridyl conjugates of calix[4]arene (L1 and L2) as
primary fluorescence switch on sensors for Zn2+ in solution and in HeLa
Cells, and the recognition of pyrophosphate and ATP by [ZnL2]",
Inorg. Chem., 51(2012) 4994-5005, DOI:10.1021/ic202426v
- R. K. Pathak, V. K. Hinge, M. Mondal and C. P. Rao,
"Triazole-linked-thiophene conjugate of calix[4]arene: Its selective
recognition of Zn2+ and as biomimetic model in supporting the events of
the metal detoxification and oxidative stress involving metallothionein",
J. Org. Chem., 76(2011), 10039-10049, DOI:10.1021/jo201865x
- R. K. Pathak, K. Tabbasum, V. K. Hinge, and C. P. Rao, "Selective
recognition of cysteine in its free and protein bound states by the Zn2+
complex of triazole based calix[4]arene conjugate", Chem. Eur. J., 17(2011), 13999-140000, DOI: 10.1002/chem.201102791
- A. Bandela, J. P. Chinta and C. P. Rao, "Role of the conformational
changes brought in the arms of 1,3-Di-capped conjugate of calix[4]arene
(L) in turning on the fluorescence of L by Hg2+" Dalton Trans. 40(2011), 11367-11370. DOI:10.1039/C1DT11208B
- A. Kumar, J. P. Chinta, A. K. Ajay, M. K. Bhat and C. P. Rao,
"Synthesis, characterization, plasmid cleavage and cytotoxicity of
cancer cells by a copper(II) complex of anthracenyl-terpyridine" Dalton Trans., 40(2011) 10865-10872. DOI:10.1039/C1DT10201J (Hot article)
- R. Joseph, J. P. Chinta and C. P. Rao, "Calix[4]arene-Based
1,3-Diconjugate of Salicylyl Imine Having Dibenzyl Amine Moiety (L):
Synthesis, Characterization, Receptor Properties toward Fe2+, Cu2+, and
Zn2+, Crystal Structures of Its Zn2+ and Cu2+ Complexes, and Selective
Phosphate Sensing by the [ZnL]" Inorg. Chem., 50(2011) 7050-7058. DOI:10.1021/ic200544a
- A. Mitra, V. K. Hinge, A. K. Mittal, S. Bhakta, P. Guionneau and C.
P. Rao,
"1-(D-Glucopyranosyl-2'-deoxy-2'-iminomethyl)-2-hydroxy-naphthalene
conjugate (L): Sensing Zn2+ followed by phosphate including DNA". Chem. Eur. J., 11(2011) 8044-8047 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201100734.
- A. Bandela, J. P. Chinta, V. K. Hinge, A. Dikundwar, T. N. Guru Row
and C. P. Rao, "Recognition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and
their derivatives by 1,3-di-naphthalimide conjugate of calix[4]arene:
Emission, absorption, crystal structures and computational studies", J. Org. Chem., 76(2011) 1742-1750. DOI: 10.1021/jo1023409 .
- A. Mitra, A. K. Mittal and C. P. Rao, "Carbohydrate assisted
fluorescence turn-on gluco-imino-anthracenyl conjugate as Hg(II) sensor
in milk and blood serum milieu", Chem. Comm , 47(2011) 2565-2567 DOI: 10.1039/C0CC04967K)
- A.K. Bandela, J.P. Chinta, V.K. Hinge, A. G. Dikundwar, T. N. Guru Row and C. P. Rao, “Recognition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their derivatives by 1,3-di-naphthalimide conjugate of calix[4]arene: Emission, absorption, crystal structures and computational studies”, J. Org. Chem., 76 2011 1742-50.
- A. Acharya , B. Ramanujam, J. P. Chinta, and C. P. Rao, “1,3-Diamido-calix[4]arene Conjugates of Amino Acids: Recognition of COOH Side Chain Present in Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins by Experimental and Computational Studies”,J. Org. Chem. 76 (2011) 127-137 DOI: 10.1021/jo101759f
- A. Kumar, B. Ramanujam, N.K. Singhal, A. Mitra and C.P. Rao, “Interaction of aromatic-imino-glycoconjugates with jacalin: Experimental and computational docking studies”,Carbohydr. Res., 345 (2010) 2491-2498.
- A. Acharya, B. Ramanujam, A. Mitra and C. P. Rao, “Nano-Fibers Formed Through … Stacking of the Complexes of Glucosyl-C2-Salicyl-Imine and Phenylalanine: Characterization by Microscopy, Modeling by Molecular Mechanics and Interaction by a-Helical & b-Sheet Proteins”, ACS Nano,4 (2010) 4061-4073.
- R. K. Pathak, A. G. Dikundwar, T. N. Guru Row and C. P. Rao, “A lower rim triazole linked calix[4]arene conjugate as a fluorescence switch on a sensor for Zn2+ in blood serum milieu”, Chem. Comm.,46 (2010) 4345-47. DOI: 10.1039/c0cc00219d
- R. Joseph, J. P. Chinta and C. P. Rao, “Lower rim 1,3-di-derivative of calix[4]arene appended salicylidene imine (H2L): Experimental and computational studies of the selective recognition of H2L towards Zn2+, and sensing phosphate and amino acid by [ZnL]”, J. Org. Chem., 75(2010) 3387-95.
- R. Joseph, J. P. Chinta and C. P. Rao, “Benzothiazole appended lower rim 1,3-di-amido-derivative of calix[4]arene: Synthesis, structure, receptor properties towards Cu2+, iodide recognition and computational modelling”, Inorg. Chimica acta363 (2010) 2833-2839.
- M. Dey, A. Ali, A. Acharya & C. P. Rao, “1,3-Di-peptido-conjugates of calix[4]arene and its di-OCH3 derivatives: Synthesis, characterization and phosphate recognition”, Indian J. Chem.49B(2010) 1098-1108.
- A. Ali, R. Joseph, B. Mahieu and C.P. Rao, “Synthesis and characterization of a (1+1) cyclic Schiff base of lower rim 1,3-diderivative of p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene and its complexes of VO2+, UO22+, Fe3+, Ni2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+”, Polyhedron29 (2010) 1035-1040. DOI information: 10.1016/j.poly.2009.12.020
- M. Dey, J.P. Chinta, G.J. Long and C.P. Rao, Synthesis and characterization of the complexes of Fe(III), Co(III), Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) and UO22+ with p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene bearing two imine pendants linked through salicylyl moiety at the lower rim, Indian J. Chem.(accepted)
- A. Mitra, J.P. Chinta and C.P. Rao, 1-(D-Glucopyranosyl-2-deoxy-2-iminomethyl)-2-hydroxybenzene as chemosensor for aromatic amino acids by switch-on fluorescence, Accepted in Tetrahedron Lett. DOI: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.10.105
- R. Joseph, B. Ramanujam , A. Acharya and C.P. Rao, Lower rim 1,3-di-{bis-(2-picolyl)}amide derivative of calix[4]arene (L) as ratiometric primary sensor towards Ag+ and the complex of Ag+ as secondary sensor towards Cys: Experimental, Computational and Microscopy studies, and INHIBIT Logic Gate Properties of L J. Org. Chem.74 (2009) 8181-90. DOI: 10.1021/jo901676s
- N.K. Singhal, A. Mitra, G. Rajsekhar, M.M. Shaikh, Subodh Kumar, P. Guionneau and C.P. Rao, Role of the orientation of OH groups on sensitivity and selectivity of the interaction of M2+ with ribosyl- and galctosyl-imino-conjugates: Solution recognition studies of M2+ in MeOH and selective recognition of Cu2+ in HEPES buffer, and first crystal structure determination of dinuclear-Cu(II) complexes based on both the glyco-imino-conjugates, Dalton Transactions(2009) 8432-42.
- G.S. Baghel and C.P. Rao, Pamoic acid in forming metallo-organic framework: Synthesis, characterization and first crystal structure of a dimeric Ti(IV) complex,Polyhedron 28(2009) 3507-14.
- J.P. Chinta, A. Acharya, A. Kumar and C.P. Rao, Spectroscopy and Microscopy Studies of the Recognition of Amino Acids and Aggregation of Proteins by Zn(II) Complex of Lower Rim Naphthylidene Conjugate of Calix[4]arene, J. Phys. Chem. B.113 (2009) 12075-83.
- R. Joseph, B. Ramanujam, A. Acharya and C.P. Rao, Fluorescence Switch-on Sensor for Cu2+ by an Amide Linked Lower Rim 1, 3 -bis(2-picolyl)amine Derivative of Calix[4]arene in Aqueous Methanol, Tetrahedron Letts.50 (2009) 2735-2739. DOI: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.03.109
- R.K. Pathak, Sk.Md. Ibrahim and C.P. Rao, Selective recognition of Zn2+ in aqueous acetonitrile by salicylaldimine appended triazole linked di-derivatives of calix[4]arene by enhanced fluorescence emission: Role of terminal CH2OH moieties in conjunction with the imine in recognition, Tetrahedron Letts.50 (2009) 2730-2734. DOI: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.03.126
- A. Kumar, N.K. Singhal, B. Ramanujam, A. Mitra, N.R. Rameshwaram, S.K. Nadimpalli and C.P. Rao, C1-/C2-aromatic-imino-glyco-conjugates: Experimental and computational studies of binding, inhibition and docking aspects towards glycosidases isolated from soybean and jack bean, Glycoconjugates J.26 (4) (2009) 495-510. DOI: 10.1007/s10719-008-9199-4
- G.S. Baghel, S.M. Shaikh and C.P. Rao, Metal ion complex of di-O-picolyl derivative of 1,1-methylene-bis(2-naphthol): First crystal structure of a monomeric Cu(II) complex of bis(2-((pyridin-2-yl)methoxy)naphthalen-1-yl)methane, Inorg. Chim. Acta. 362(2009) 2770-2775. DOI: 10.1016/j.ica.2008.12.019
- A. Mitra, B. Ramanujam, and C.P. Rao, 1-(D-glucopyranosyl-2-deoxy-2-iminomethyl)-2-hydroxynaphthalene as chemo-sensor for Fe3+ in aqueous HEPES buffer based on colour changes observable by naked eye, Tetrahedron. Letts., 50 (2009) 776-780.
- G.S. Baghel, B. Ramanujam and C.P. Rao, Selective Recognition of Cu2+ by Di-O-picolyl Derivative of 1,1'-Methylene-Bis(2-Naphthol), J. Photochem. Photobiol. A202 (2009) 172-177.
- R. Joseph, B. Ramanujam, H. Pal and C.P. Rao, Lower rim 1,3-di-derivative of calix[4]arene possessing bis-{N-(2-2-dipyridylamide)} pendants: An unusual dual fluorescence sensor for Zn2+ and Ni2+, Tet. Lett.49(2008) 6257-61.
- R. Joseph, B. Ramanujam, A. Acharya, A. Khutia and C.P. Rao, Experimental and Computational Studies of Selective Recognition of Hg2+ by Amide Linked Lower Rim 1, 3-di-benzimidazole Derivative of Calix[4]arene: Species Characterization in Solution and that in the Isolated Complex, Including the Delineation of the Nano-Structures, J. Org. Chem.73 (2008) 5745-58.
- A. Ali, C.P. Rao and P. Guionneau, Influence of alkali and alkaline earth ions on the O-alkylation of the lower rim phenolic-OH groups of p-tert-butyl-calix[4]arene to result in amide-pendants: Template action of K+ and the structure of K+ bound tetra-amide derivative crystallized with a p-tert-butyl-calix[4]arene anion, J. Chem. Sci., 120 (2008) 237-247.
- R. Joseph, A. Gupta, A. Ali and C.P. Rao, Fluorescence and absorption studies on the selective recognition of iodide by lower rim 1,3-bis(aminoethoxy)-p-t-butyl-calix[4]arene derivative, Indian J. Chem.46A (2007) 1095-1100.
- R. Ahuja, N.K. Singhal, B. Ramanujam, M. Ravikumar, and C.P. Rao, Experimental and Computational Studies of the Recognition of Amino Acids by Galactosyl-imine and -amine Derivatives: An Attempt to Understand the Lectin-Carbohydrate Interactions, J. Org. Chem.,72 (2007) 3430-3442
- R. Joseph, A. Gupta and C.P. Rao, Photophysical properties of the interaction of lower rim 1,3-bis(aminoethoxy)-calix[4]arene derivative with Pb2+, Hg2+ and Cd2+ions: Recognition of Hg2+, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A, 188 (2007) 325-328.
- N.K. Singhal, B. Ramanujam, V. Mariappandar and C.P. Rao, Carbohydrate-Based Switch-On Molecular Sensor for Cu(II) in Buffer: Absorption and Fluorescence Study of the Selective Recognition of Cu(II) Ions by Galactosyl Derivatives in HEPES Buffer, Org. Lett., 8 (2006) 3525-28.
- R. Ahuja, N.K. Singhal and C.P. Rao, Lectins: Chemical, structural and biological aspects including drug targeting, Khimiya/Chemistry. A Bulgarian J. Chem. Edn., 15(2006) 275-304.
- A. Ali, S. Salunke-Gawali, C.P. Rao and J. Linares, Mono- and di-nuclear Cu(II) complexes of p-tert-butyl-calix[4]arene-1,3-diacid derivative: A comparative study of their characterization and catecholase mimetic activity, Indian J. Chem.,45A (2006) 853-857.
- A. Kumar, A. Ali, C.P. Rao, Photo-physical behavior as chemosensor properties of anthracene-anchored 1,3-di-derivatives of lower rim calix[4]arene towards divalent transition metal ions, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A,177(2006) 164-169.
- A. Ali, S.J.S. Flora, Geetu Saxena, E. Kolehmainen, B. Mahieu and C.P. Rao , Synthesis and characterization of Sn(IV) complexes of lower rim 1,3-diacid derivative of calix[4]arene and their protective effects on tissue oxidative stress and essential metal concentration in lead exposed male Wistar rats, J. Inorg. Biochem.,100 (2006) 206-213.
- M. Dey, C.P. Rao and P. Guionneau, Structural characterization and reactivity of Cu(II) complex of p-tert-butyl-calix[4]arene bearing two imine pendants at lower rim, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 8 (2005) 998-1001.
- J. Dessingou, R. Joseph and C.P. Rao, A direct fluorescence-on chemo-sensor for selective recognition of Zn(II) by a lower rim 1,3-di-derivative of calix[4]arene possessing bis-{N-(2-hydroxynaphthyl-1-methylimine)} pendants, Tetrahedron Letts., 46 (2005) 7967-7971.
- A. Ali and C.P. Rao, Formation of mono- and di-amide-calix[4]arene derivatives from the reaction of p-tert-butyl-calix[4]arene and a-chloro-N,N-diethylacetamide in the presence of sodium hydride, Indian J. Chem., 44B (2005) 549-552.
- A. Ali, S. Salunke-Gawali, C. P. Rao, J. Linares, A first report of the complexes of 5,11,17,23-tetra-tert-butyl-25,27-diethoxycarboxymethoxy-26,28-dihydroxycalix[4]arene with Mn(II), Fe(III), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II), Inorg. Chem. Commun., 7 (2004) 1298-1301.
- G. Rajsekhar, C. P. Rao, P. Saarenketo, K. Nttinen, and K. Rissanen, Complexation Behaviour of Hexadentate Ligands Possessing N2O4 and N2O2S2 Cores: Differential Reactivity Towards Co(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) Salts and Structures of the Products, New J. Chem., 28 (2004) 75-84.
- C.P. Rao and M. Dey, Calixarenes: Smart Molecular Hosts, Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 1(2003)475-497.
- M. Dey, C.P. Rao, P.K. Saarenketo, K. Rissanen, E. Kolehmainen, and P. Guionneau, Mn(IV) and Co(III)-complexes of OH-rich ligands possessing O2N, O3N and O4N cores: syntheses, characterization and crystal structures, Polyhedron, 22 (2003) 3515-3521.
- A. K. Sah, A. Ali, E. K. Wegelius, K. Rissanen and C. P Rao, A soluble complex of Zn(II) with N2O4 core: A structural study, Indian J. Chem., 42A (2003) 1888-1891.
- G. Rajsekhar, A. K. Sah, C.P. Rao, P. Guionneau, M. Bharathy, and T. N. GuruRow, Bis-(m-saccharide-C-2-oxo) Dinuclear Cu(II) Complexes of 4,6-O-butylidene/ethylidene-N-(a-hydroxynapthylidene/o-hydroxybenzylidene/5-bromo-o-hydroxybenzylidene)-b-D-glucopyranosylamine: Structural Aspects and Data Correlations, Dalton Transactions (2003) 3126-3135.
- G. Rajsekhar, C.P. Rao, K. Nttinen and K. Rissanen, Unusual interaction extended between the pyranose ring oxygen and Zn(II) center in the complexes derived from 4,6-Obutylidene/ethylidene-N-(a-hydroxynaphthylidene/o-hydroxybenzylidene)-b-D-glucopyranosylamine: Evidence for a pseudo-bicapped tetrahedral complex of Zn(II) based on the crystal structure Inorg. Chem. Commun., 6 (2003) 1156-60.
- T.M. Das, C.P Rao, N. Kalle and K. Rissanen , Synthesis and crystallographic characterization of some derivatives of benzimidazole, Indian J. Chem., 42B(2003) 661-665.
- C.P. Rao and T. Mohan Das, Saccharide complexes of lanthanides, Indian J. Chem., 42A (2003) 227-239.
- G. Rajsekhar, C.P. Rao and P. Guionneau, First crystallographic evidence for the formation of b-D-ribopyranosylamine from the ammonialysis of D-ribose, Carbohydr. Res. 338 (2003) 801-805.100. P. V. Rao, C. P. Rao, E.K. Wegelius and K. Rissanen, 2-Hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde derived Schiff bases: synthesis, characterization and structure, J. Chem. Cryst., 33 (2003) 139-147
- P. V. Rao, C. P. Rao, E.K. Wegelius and K. Rissanen, 2-Hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde derived Schiff bases: synthesis, characterization and structure, J. Chem. Cryst., 33(2003) 139-147.
- M. Dey, C. P. Rao, P. K. Saarenketo, and K. Rissanen, Mono-, Di- and Tri-nuclear Ni(II) Complexes of N-, O- Donor ligands: Structural Diversity and Reactivity, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 5(2002) 924-928.
- C.P. Rao and T. Mohan Das, Simple perspectives of carbohydrates, Khimiya/Chemistry. A Bulgarian J. Chem. Edn., 11 (2002) 385-419.
- G. Rajsekhar, U.B. Gangadharmath, C.P. Rao, P. Guionneau, P.K. Saarenketo, and K. Rissanen, Synthesis and characterization of 4,6-Obutylidene-N-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-b-D-glucopyranosylamine: Crystal structures of 4,6-Obutylidene-a-D-glucopyranose, 4,6-Obutylidene-b-D-glucopyranosylamine and 4,6-Obutylidene-N-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-b-D-glucopyranosylamine, Carbohydr. Res.337 (2002) 1477-84.
- G. Rajsekhar, C.P. Rao, P.K. Saarenketo, E. Kolehmainen and K. Rissanen, C-S bond cleavage by cobalt: Synthesis, Characterization and Crystal structure determination of 1,2-di-(o-salicylaldiminophenylthio)-ethane and its Co(III) product with C-S bond cleaved fragments, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 5 (2002) 649-652.
- A. Mukhopadhyay, E. Kolehmainen, C.P. Rao, Synthesis and characterisation of saccharide complexes of La(III) ion, Indian J. Chem. 41A(2002) 1621-24.
- M. Dey, C.P. Rao, P. Saarenketo, K. Rissanen and E. Kolehmainen, Four-, Five- and Six Coordinated Zn(II)-complexes of OH-containing ligands: Syntheses, Structure and Reactivity, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., (2002) 2207-2215.
- M. Dey, C.P. Rao, P.K. Saarenketo and K. Rissanen, Synthesis, Structural Diversity, Inter-conversion and Reactivity of Cu(II) Complexes of hydroxy-rich molecules, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 5 (2002) 380-383.
- A.K. Sah, C.P. Rao, P.K. Saarenketo, K. Rissanen, G.A. van Albada and J. Reedijk, Dinuclear Copper Complexes of N-(2-Hydroxybenzylidene or 5-Bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-4,6-O-ethylidene-b-D-glucopyranosylamine: Coordination Variation and Structural Diversity, Chem. Letts. (2002) 348-349.
- T.M. Das, C.P. Rao, E. Kolehmainen, R.M. Kadam and M.D. Sastry, Interaction of metal ions with D-glucobenzothiazoline: Isolation and characterization of the resultant products, Carbohydr. Res., 337 (2002) 289-296.
- G. Rajsekhar, C.P.. Rao, P.K Saarenketo, E. Kolehmainen and K. Rissanen, Glycosylaminesof 4,6-O-butylidene-a-D-glucopyranose: Synthesis and characterization of glycosylamines, and the crystal structure of 4,6-Obutylidene-N-(o-chlorophenyl)-b-D-glucopyranosylamine, Carbohydr. Res., 337 (2002) 187-194.
- A.K. Sah, C.P. Rao, P.K. Saarenketo and K. Rissanen, Crystal structure of N-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-4,6-O-ethylidene-b-D-glucopyranosylamine, Carbohydr. Res.,337 (2002) 79-82
- P.V. Rao, E. Kolehmainen and C.P. Rao, Synthesis, characterization and structure of Ti(IV) complexes of hydroxy-rich ligands, Ind. J. Chem., (2002) 284-289.
- A.K. Sah, C.P. Rao, P.K. Saarenketo and K. Rissanen, Structure of the First Tetranuclear Ni(II) Complex Derived From N-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-4,6-O-ethylidene-b-D-glucopyranosylamine, Chem. Lett., (2001) 1296-97.
- A.K. Sah, C.P. Rao, E.K. Wegelius, E. Kolehmainen and K. Rissanen, Synthesis, characterization and first crystal structure of Zn(II) complex of N-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-4,6-O-ethylidene-b-D-glucopyranosylamine, Carbohydr. Res., 336 (2001) 249-255.
- P. V. Rao, C. P. Rao, E. Kolehmainen, E. K. Wegelius and K. Rissanen, Lower Rim 1,3-Di-derivatives of Calix[4]arene Amides Having Amino Acid Ester and Amines as Pendants, Chem. Lett., (2001) 1176-77.
- T. Mohan Das, C.P. Rao and E. Kolehmainen, Interaction of metal ions with N-glycosyl amines: Isolation and characterization of the products of 4,6-O-benzylidene-N-(o-carboxyphenyl)-b-D-glucopyranosylamine with different metal ions, Carbohydr. Res., 335 (2001) 151-158.
- A.K. Sah, C. P. Rao, P. K. Saarenketo, E. Kolehmainen and K. Rissanen, Synthesis, characterization and crystal structures of Schiffs bases obtained from the reactions of 4,6-O-ethylidene-b-D-glucopyranosylamine with substituted salicylaldehydes, Carbohydr. Res.,335 (2001) 33-43.
- T.M. Das, C. P. Rao, and E. Kolehmainen , Synthesis and Characterization of N-glycosyl amines obtained from the reaction between 4,6-O-benzylidene-D-glucopyranose and substituted aromatic amines, and also between 2-(o-aminophenyl)benzimidazole and pentoses or hexoses, Carbohydr. Res., 334 (2001) 261-269.
- A. K. Sah, C P. Rao, P. K. Saarenketo, E. K. Wegelius, E. Kolehmainen and K. Rissanen, First Crystallographic investigation of complexes of cis-VO2+, cis-MoO22+ and trans-UO22+ species with Schiffs base molecules derived from 4,6-O-ethylidene-b-D-glucopyranosylamine, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., (2001) 2773-2781.
- A. Mukhopadhyay, E. Kolehmainen and C.P. Rao, Lanthanide-saccharide chemistry: Synthesis and characterisation of saccharide complexes of Sm(III) (f5), Eu(III) (f6) and Dy(III) (f9) ions, Indian J. Chem.,40A (2001) 1045-1052.
- A.K. Sah, C.P. Rao, P.K. Saarenketo, E.K. Wegelius, K. Rissanen and E. Kolehmainen, N-Glycoside of ortho substituted anilines of 4,6-O-Ethylideneglucopyranose: Synthesis, characterization and structure of COOH, -Cl and F substituted glycosylamines and metal ion complexes of COOH derivative. Dalton Transactions (2000) 3681-3687.
- A. Mukhopadhyay, E. Kolehmainen and C.P. Rao, Interaction of saccharides with rare earth metal ions: Synthesis and characterisation of Pr(III)- and Nd(III)-saccharide complexes, Carbohydr. Res., 328 (2000) 103-113.
- P.V. Rao, C.P. Rao, A. Sreedhara, E.K. Wegelius, K. Rissannen and E. Kolehmainen, Synthesis, structure and reactivity of trans-UO22+ complexes of OH-containing ligands, Dalton Transactions, (2000) 1213-1218.
- A. Mukhopadhyay, E. Kolehmainen and C.P. Rao, Lanthanide-saccharide chemistry: Synthesis and characterisation of Ce(III)-saccharide complexes, Carbohydr. Res.,324 (2000) 30-37.
- C.P. Rao, K. Geetha, M.S.S. Raghavan, A. Sreedhara, K. Tokunaga, T. Yamaguchi, V. Jadhav, K.N. Ganesh, T. Krishnamoorthy, K.V.A. Ramaiah and R.K. Bhattacharyya, Transition metal saccharide chemistry and biology: Syntheses, characterisation, solution stability and putative bio-relevant studies of iron-saccharide complexes, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 297(2000) 373-382.
- P.V. Rao, C.P. Rao, E.C. Wegelus, E. Kolehmainen and K. Rissanen, Reactivity of cis-dichloro-bis(acetylacetonato)titanium(IV) towards hydroxy(-OH)-containing ligands: Reactivity, and isolation and characterisation of products, Dalton Transactions, (1999) 4469-4474.
- C.P. Rao and A. Sreedhara, Oxo-metal complexes of alkoxo rich ligands and reactivity of vanadium complexes, Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Chem. Sci.), 111 (1999) 479-487.
- C.P. Rao, A. Sreedhara, P. V. Rao, N.K. Lokanath, M.A. Sreedhar, J.S. Prasad and K. Rissanen, Recognition of oxovanadium(V) species and its separation from other metal species through solution complexation by some acyclic ligands, Polyhedron , 18 (1999).289-297.
- C.P. Rao, Symmetry and spectroscopy of molecules, by K. Veera Reddy (New Age Internation (P) Limited Publishers, New Delhi) a book review, Indian J. Chem., 37A(1998) 848.
- C.P. Rao, Symmetry and spectroscopy of molecules, by K. Veera Reddy (New Age Internation (P) Limited Publishers, New Delhi) a book review, Indian J. Chem., 37A (1998) 848.
- H. Arakawa, N. Watanabe, R. Tamura and C.P. Rao, Reduction of potassium chromate by tannins, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 7 1 (1998) 1993-1998.
- C.P. Rao, A. Sreedhara, P.V. Rao, M. B. Verghese, K. Rissannen, E. Kolehmainen, N.K. Lokanath, M.A. Sreedhar and J.S. Prasad, Synthesis, structure, reactivity and species recognition of oxovanadium(V) and molybdenum(VI) complexes, J.C.S. Dalton Trans., (1998) 2383-93.
- C.P. Rao, S.P. Kaiwar and M.S.S. Raghavan, Chromium toxicity: Spectral and electrochemical stuides of Cr(VI) reduction by biomimicking molecules. Comparisons and correlations, Int. J. Environ. Studies, 54B (1998) 131-144.
- T. Krishnamoorthy, A. Sreedhara, C.P. Rao and K.V.A. Ramaiah, Reducing agents mitigate protien synthesis inhibition mediated by various vanadate and vanadyl compounds in reticulocyte lysates, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 349 (1998) 122-128.
- R. P. Bandwar, S. J. S. Flora,and C. P. Rao. Influence of Zinc-saccharide complexes on some haematological parameters in rats BioMetals, 10 (1997) 337-341.
- R.P. Bandwar and C. P. Rao, Transition metal-saccharide chemistry and biology: An emerging field of multidisciplinary interest, Curr. Sci. (India), 72 (1997) 788-796.
- A. Sreedhara, N. Susa and C. P. Rao, Vanadate and Chromate reduction by saccharide and L-ascorbic acid: Effect of the isolated V(IV) and Cr(III) products on DNA nicking. Lipid peroxidation, cytotoxicity and on enzymatic & non-enzymatic antioxidants, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 263 (1997) 189-194.
- R. P. Bandwar and C. P. Rao, Transition metal saccharide chemistry and biology: Vanadyl-monosaccharide complexes and their in vitro effect on pUC-18 DNA,J. Inorg. Biochem, 68 (1997) 1-6.
- C.P. Rao, Metal-ligand interactions: Structure and reactivity, ed. By Nino Russo and Dennis R. Salahub (Kluwar Academic Publishers, The Netherlands) a book review, Indian J. Chem., 36A (1997) 354.
- R. P. Bandwar and C. P. Rao, Transition metal saccharide chemistry: Synthesis and characterization of D-Glucose, D-Fructose, D-Galactose, D-Xylose, D-Ribose and Maltose complexes of Ni(II), Carbohydr. Res., 297 (1997) 341-346.
- R. P. Bandwar, M. D. Sastry, R. M. Kadam and C. P. Rao, Transition metal saccharide chemistry: Synthesis and characterization of D-Glucose, D-Fructose, D-Galactose, D-Xylose, D-Ribose and Maltose complexes of Co(II), Carbohydr. Res., 297 (1997) 333-339.
- R. P. Bandwar, M. Giralt, J. Hidalgo, C. P. Rao and G. U. Kulkarni, Transition metal saccharide chemistry and biology: Saccharide complexes of Cu(II) and their in vivo metallothionein synthesis in mice, J. Inorg. Biochem., 66 (1997) 37-44.
- G. Asgedom, A. Sreedhara, J. Kivikoski and C. P. Rao, Synthesis and characterization of dimeric vanadyl(IV) complexes of Schiff bases derived from anthranilic acid and salicylaldehyde (or its derivatives) or acetylacetone. Single crystal X-ray structure of the oxidized products, Polyhedron, 16(1997) 643-651.
- A. Sreedhara, N. Susa, A. Patwardhan and C. P. Rao, One electron reduction of vanadate(V) to oxovanadium(IV) by low molecular weight biocomponents like saccharides and L-ascorbic acid: Effect of oxovanadium(IV) complexes on pUC18 DNA and on lipid peroxidation in isolated rat hepatocytes, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 224 (1996) 115-120.
- G. Asgedom, A. Sreedhara, J. Kivikoski, J. Volkonen, E. Kolehmeinen and C. P. Rao, Alkoxo bound monooxo and dioxovanadium(V) complexes: Synthesis, characterization, X-ray structure, and solution reactivity studies. Inorg. Chem. 35 (1996) 5674-5683.
- A. Sreedhara, C. P. Rao and B. J. Rao, Transition metal saccharine chemistry and biology: Synthesis, charaterization, electrochemistry and epr studies of oxo-vanadium(IV) complexes of saccharides and their derivatives and in vitro interaction of some of these with ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease. Carbohydr. Res.,289 (1996) 39-53.
- G. Asgedom, A. Sreedhara, C.P. Rao and E. Kolehmainen, Monooxovanadium(V) mixed ligand complexes of Schiff bases and catecholates: Synthesis, spectral and electrochemical characterization, Polyhedron, 15 (1996) 3731-3739.
- R. P. Bandwar and C. P. Rao, Transition metal-saccharide chemistry: synthesis and charaterization of D-Galactose, D-Fructose, D-Glucose, D-Xylose, D-Ribose and Maltose complexes of Mn(II), Carbohydr. Res., 287(1996) 157-168.
- R. P. Bandwar, M. Giralt, J. Hidalgo and C. P. Rao, Metal-saccharide chemistry and biology: Saccharide complexes of Zinc and the effect of some complexes on Metallothionein synthesis in Mice Carbohydr. Res., 284(1996) 73-84.
- S. P. Kaiwar, A. Sreedhara, M. S. S. Raghavan, C. P. Rao, V. Jadhav and K. N. Ganesh, Synthesis, Characterization and DNA interaction studies of Cr(III) products isolated from Cr(VI) reduction with SH containing molecules, Polyhedron, 15 (1996) 765-774.
- G. Asgedom, A. Sreedhara,J. Kivikoski, E. Kolehmeinen and C. P. Rao, Synthesis, Structure, spectral characterization and Photoreactivity studies of monomeric Dioxovanadium(V) Schiff base complexes of trigonal bipyramidal geometry, J.C.S. Dalton Trans., (1996) 93-97.
- R. P. Bandwar and C. P. Rao, Role of saccharides in reduction and complexation of transition metal ions and the effect of zinc saccharides on some haematological variables, Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Chem. Sci.), 108 (1996) 312-312.
- R. P. Bandwar and C. P. Rao, In vitro relative reducing abilities of some hydroxy containing compounds including monosaccharides towards V(V) and Mo(VI), Carbohydr. Res., 277 (1995) 197-207.
- G. Asgedom, A. Sreedhara, J. Kivikoski, J. Volkonen and C. P. Rao, Mononuclear cis-Dioxo(V) anionic complexes [VO2L]- {H2L = =[1+1] schiff base derived from salicyladehyde (or substituted derivatives) & 2-amino-2-methylpropan-1-ol}: Synthesis, structure, spectroscopy, electrochemistry and reactivity studies, J.C.S. Dalton Trans., (1995) 2459-2466.
- K. Geetha, M. S. S. Raghavan, S. K. Kulshrestha, R. Sasikala and C. P. Rao, Transition-metal saccharide chemistry: Synthesis, spectroscopy , electrochemistry and magnetic susceptibility studies of Fe(III) complexes of mono and disaccharide, Carbohydr. Res., 271 (1995) 163-175.
- S. P. Kaiwar, M. S. S. Raghavan and C. P. Rao, Transition-metal saccharide chemistry and biology: synthesis, characterisation, redox behaviour, Biointeraction and data correlations of Dinuclear Chromium(III) complexes, J.C.S. Dalton Trans., (1995) 1569-1576.
li> G. Asgedom, A. Sreedhara and C. P. Rao, OxoV(V) Schiff Base complexes of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane with salicylaldehyde and its derivatives: Synthesis, characterization and redox reactivity, Polyhedron, 14 (1995) 1873-1879.
- S.P. Kaiwar and C.P. Rao, In vitro reduction of Cr(VI) by low molecular weight biomimetic components: A comparative study using UV-Vis spectroscopy, Chem.-Biol. Int., 95 (1995) 89-96.
- R.P. Bandwar, M.S.S. Raghavan and C.P. Rao, Transition-metal saccharide complexes of Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II), BioMetals, 8(1995) 19-24.
- A. Sreedhara, M.S.S. Raghavan and C.P. Rao, Transition-metal saccharide interactions: Synthesis and characterisation of vanadyl saccharides , Carbohydr. Res. 264 (1994) 227-235.
- C.P. Rao, S.P.Kaiwar and M.S.S. Raghavan, Transition-metal saccharide chemistry: Synthesis, characterisation, electrochemistry and magnetic studies of Cr(III)-hexose complexes and their in vitro interaction with DNA , Polyhedron, 13 (1994) 1895-1906.
- S.P. Kaiwar, R.P. Bandwar, M.S.S. Raghavan and C.P. Rao, Transition-metal saccharide chemistry: Synthesis and characterisation of some monosaccharide complexes , Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Chem. Sci. ), 106 (1994) 743-752.
- S.P. Kaiwar, M.S.S. Raghavan and C.P. Rao, In vitro reducing abilities of various hydroxy-containing molecules including saccharides and its derivatives towards chromates , Carbohydr. Res, 256 (1994) 29-40.
- C.P. Rao, K. Geetha and M.S.S. Raghavan, Fe(III) complexes of D-glucose and D-fructose , BioMetals, 7 (1994) 25-29.
- C.P. Rao and S.P. Kaiwar, Reduction of potassium chromate by D-fructose, D-galactose, D-mannose, D-glucose and L-sorbose , Carbohydr. Res, 244 (1993) 15-25
- J. D. Protasiewicz, P. A. Bianconi, I. D. Willliams, S. Liu, C.P. Rao and S. J. Lippard, Synthesis and structural characterisation of low-valent Group V phosphine complexes , Inorg. Chem.,31 (1992) 4134-4142.
- S.P. Kaiwar and C.P. Rao, Soluble complexes of early first-row transition-metal ions with D-glucose , Carbohydr. Res 237 (1992) 203-210.
- C. P. Rao and S.P. Kaiwar, Chromate reduction: Reduction of potassium chromate by D-glucose and D-fructose to form Cr(III)- saccharide complexes , Carbohydr. Res,237 (1992) 195-202.
- C.P. Rao, K. Geetha and R.P. Bandwar, Solution stability of iron-saccharide complexes , Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett, 2 (1992) 997-1002.
- R.N. Vrtis, S. Liu, C.P. Rao, S.G. Bott and S. J. Lippard, Mechanistic studies of the reductive coupling of CO in seven coordinated Nb(I) and Ta(I) dicarbonyl complexes, Organometallics, 10 (1991) 275-285.
- C. P. Rao Fabrication of simple, sturdy and inexpensive controlled-atmosphere glove box for routine use , Res. & Ind., 36 (1991) 188-190.
- C.P. Rao and S.P. Kaiwar, Homoleptic glucose complexes of VO2+ and Cr3+ , Inorg. Chim. Acta, 186(1991) 11-12.
- C.P. Rao, P.S. Sarkar, S.P. Kaiwar and S. Vasudevan, Chromate reductase activity: Characterisation of Cr(VI) to Cr(III) conversion , Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci. (Chem. Sci.) 102 (1990) 219-230.
- J. S. Svendsen, I. Marko, E. N. Jacobsen, C.P. Rao, S. Bott and K. B. Sharpless, On the structure of osmium tetraoxide-cinchona alkaloid complexes , J. Org. Chem, 54 (1989) 2263-2264.
- C.P. Rao, Easy and economic ways of handling crystals for X-ray diffraction studies , J. Appl. Cryst. 22 (1989) 182-183.
- R. N. Vrtis, , C.P. Rao, S. G. Bott and S. J. Lippard, Synthesis and stabilisation of tantalum-coordinated dihydroxyacetylene from two reductively coupled carbon monoxide ligands , J. Am. Chem. Soc. 110 (1988) 7564-7566.
- G. M. Villacorta, C.P. Rao and S. J. Lippard, Synthesis and reactivity of binuclear tropocoronand and related organocopper(I) complexes. Catalytic enantioselective conjugate addition of Grignard reagents to 2-cyclohexan-1-one , J. Am. Chem. Soc.,110 (1988) 3175-3182.
- R.N. Vrtis, C.P. Rao, S, Warner and S. J. Lippard, Carbynes generated from metal carbonyl and isocyanide complexes: Intermediates in the reductive coupling of CO and CNR ligands , J. Am. Chem. Soc. 110 (1988) 2669-2670.
- P.A. Bianconi, R.N. Vrtis, C.P. Rao, I.D. Williams, M.P. Engeler and S.J. Lippard, Reductive coupling of CO ligands to form coordinated bis(trimethylsiloxy)ethyne in seven-coordinate Nb(I) and Ta(I) [M(CO)2(dmpe)2Cl] complexes, Organometallics,6 (1987) 1968-1977.
- R.N. Mukherjee, C.P. Rao and R.H. Holm, Solution chemistry of ethane-1,2-dithiolate complexes: Equilibria and electron-transfer reactions, Inorg. Chem., 25 (1986) 2979-2989.
- B.S. Snyder, C.P. Rao and R.H. Holm, Mono- and bi-nuclear metal(II) complexes of ethane-1,2-dithiolate complexes: Preparation, equilibrium and redox properties of [Ni(S2C2H4)2]2- and [Ni2(S2C2H4)3]2- , and the structure of [Ni2(S2C2H4)3]2- and [Pd(S2C2H4)2]2-, Aust. J. Chem.,39 (1986) 963-974.
- C.P. Rao, J.R. Dorfman and R.H. Holm, Synthesis and structural systematics of ethane-1,2-dithiolato complexes, Inorg. Chem.,25(1986) 428-439.
- A.D. Watson, C.P. Rao, J.R. Dorfman and R.H. Holm, Systematic stereochemistry of metal(II) thiolates: Synthesis and structures of [M2(S2C2H5)6]2- (M = Mn(II), Ni(II), Zn(II), Cd(II), Inorg. Chem., 24 (1985) 2820-2826.
- J.R. Dorfman, C.P. Rao and R.H. Holm, Structural diversity of homoleptic ethane-1,2-dithiolate complexes of the first transition series, Inorg. Chem.,24 (1985) 453-454.
- C.P. Rao, A.M. Rao and C.N.R. Rao Crystal and molecular structures of alkali- and alkaline-earth-metal complexes of N,N-dimethylformamide, Inorg. Chem.,23(1984) 2080-2085.
- C.P. Rao, P. Balaram and C.N.R. Rao, C-13 nmr studies of the conformational changes in proline oligomers brought about by lithium and calcium salts, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 5 (1983) 289-294.
- C.P. Rao, P. Balaram and C.N.R. Rao, Infrared spectroscopic study of C7 intramolecular hydrogen bonds in peptides, Biopolymers., 22 (1983) 2091-2104.
- C.P. Rao and V.R.S. Rao, Application of sub- and super-equivalence method of the reverse isotope dilution analysis. Determination of Tl(III) and Tl(I) using ferroin and diethyldithiocarbamate, Radiochem. Radioanl. Letts., 57 (1983) 65-72.
- C.P. Rao and P. Balaram, Molecular structure of t-Boc-Leu-Aib-Pro-Val-Aib-OMe, a fragment of alamethicin and suzukacillin: A 310-helical pentapeptide, Biopolymers.,21 (1982) 2461-2472.
- A.K. Francis, C.P. Rao, M. Iqbal, R. Nagaraj, M. Vijayan and P. Balaram, Helical conformations of three crystalline pentapeptide fragments of suzukacillin, a membrane channel forming polypeptide Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 106 (1982) 1240-1247.
- C.P. Rao, N. Shamala, R. Nagaraj, C.N.R. Rao and P. Balaram, Hydrophobic channels in crystals of an -aminobutyric acid pentapeptide, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 103 (1981) 898-904.
- C.P. Rao, R. Nagaraj, C.N.R. Rao and P. Balaram, Infrared studies on the conformation of synthetic alamethicin fragments and model peptides containing -aminoisobutyric acid, Biochemistry (USA),19(1980) 425-431.
- C.P. Rao, P. Balaram and C.N.R. Rao, C-13 NMR studies of the binding of alkali and alkaline earth metal salts to amides, J.C.S. Faraday I,76(1980) 1008-1013.
- C.P. Rao, R. Nagaraj, C.N.R. Rao and P. Balaram, Infrared spectroscopy as a probe for the development of secondary structure in the amino-terminal segment of alamethicin, FEBS Letts., 100 (1979) 244-248.
- C.N.R. Rao, U.P. Agarwal, C.P. Rao and J.R. Fernandes, Study of methanol, 2-methyl-2-propanol, and formamide and their electrolyte solution by Infrared spectroscopy, J. Phys. Chem., 83 (1979) 722-728.
- V.R.S. Rao, C.P. Rao and G. Tataiah, Radiometric titrations of Tl(III) with EDTA, Radiochem. Radioanal. Letts.,33 (1978) 1-6.
- V.R.S. Rao, C.P. Rao and G. Tataiah, sub and super equivalence method of reverse isotope dilution analysis, Radiochem. Radioanal. Letts.,30 (1977) 365-370.
- V.R.S. Rao, C.P. Rao and G. Tataiah, Determination of thallium using brilliant green by sub and super equivalence method of isotope dilution analysis, Radiochem. Radioanal. Letts., 29 (1977) 261-266.
- V.R.S. Rao, C.P. Rao and G. Tataiah, Determination of thallium by sub- and super-equivalence method of isotope dilution analysis, Radiochem. Radioanal. Letts.,29 (1977) 43-46.



























































